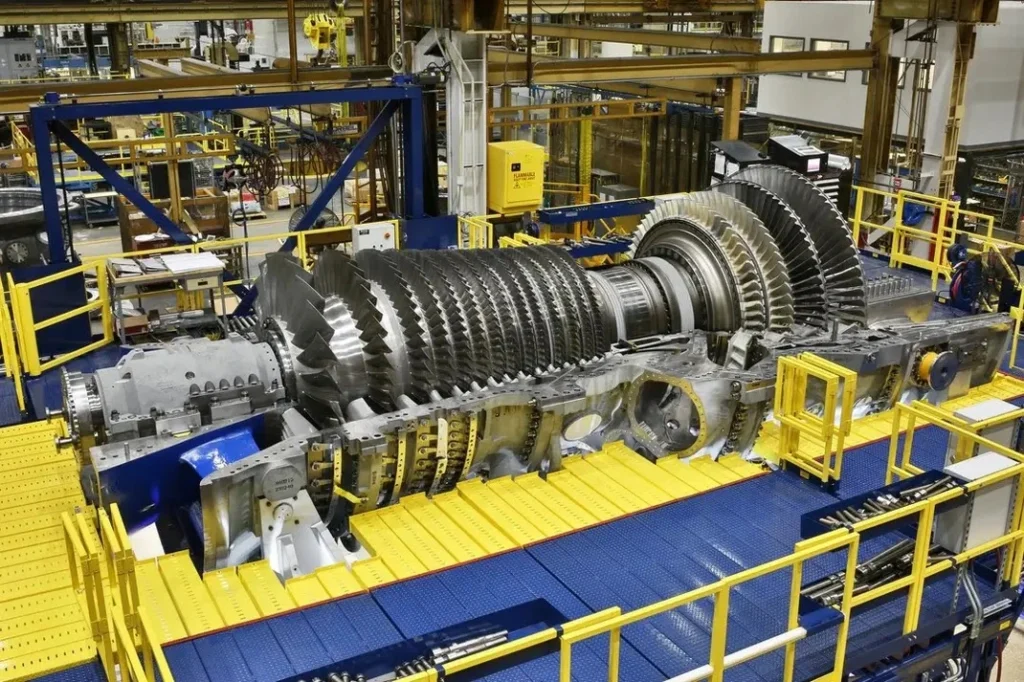

Steam Power Plants: Steam turbines are critical components in power generation, converting thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy, which is then used to generate electricity. These machines are found at the heart of power plants, playing a crucial role in meeting global energy demands.
Importance in Power Generation: In today’s energy landscape, steam turbines are pivotal, especially in large-scale power generation, where they contribute significantly to the global energy supply. Their efficiency and reliability make them indispensable in both traditional fossil fuel-based and modern nuclear power plants.
Purpose of the Document: This document aims to provide an in-depth exploration of Impulse and Reaction Steam Turbines, discussing their design, operation, and applications. By the end, readers will have a comprehensive understanding of how these turbines work and their relevance in power generation.
2. Fundamentals of Steam Turbines
Basic Principles of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines operate on the principle of converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. Steam, produced in boilers, is expanded through the turbine blades, creating mechanical rotation. This rotational energy is then converted into electrical energy using generators.
Historical Development: The evolution of steam turbines dates back to the late 19th century, with Charles Parsons and Gustaf de Laval pioneering designs. The progression from simple steam engines to highly efficient steam turbines marked a significant leap in industrial power generation capabilities.
Types of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines are generally classified into two main types: Impulse and Reaction turbines. Both types utilize the expansion of steam, but they differ fundamentally in how the energy conversion takes place.
Overview of Impulse and Reaction Turbines: Impulse turbines utilize high-velocity jets of steam to impart force directly on turbine blades, causing rotation. Reaction turbines, on the other hand, rely on the expansion of steam within the blades themselves, where the reaction force drives the turbine.
3. Impulse Steam Turbines
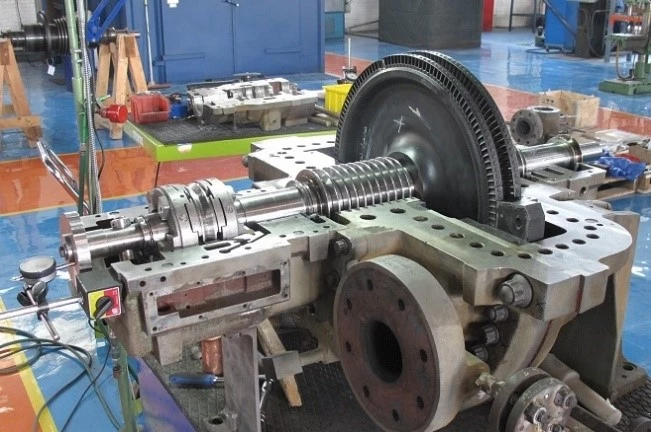

Definition and Working Principle: Impulse turbines operate based on Newton’s Third Law of Motion, where the action of a steam jet imparts an equal and opposite reaction on the turbine blades, causing rotation. The steam’s kinetic energy is fully converted to mechanical energy before it leaves the nozzle, and there is no further expansion in the moving blades.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion: This law forms the foundation for impulse turbines. When steam exits a nozzle at high velocity, it strikes the turbine blades, transferring momentum and causing the rotor to spin.
- Energy Conversion Process: In an impulse turbine, steam is expanded in a nozzle, converting pressure energy into kinetic energy. The high-speed steam jets then strike the blades, transferring kinetic energy to the rotor.
Design and Construction: Impulse turbines feature distinct components designed to maximize efficiency and power output.
- Blades and Nozzles: The design of the blades and nozzles is crucial. Nozzles accelerate steam to high velocities, while blades are shaped to effectively capture the kinetic energy from the steam jets.
- Rotor and Stator Arrangement: The rotor, attached to the shaft, carries the moving blades, while the stator holds the stationary blades or nozzles. This arrangement ensures efficient energy transfer and rotational motion.
- Material Considerations: The materials used in construction must withstand high temperatures and pressures. High-strength alloys and corrosion-resistant coatings are typically employed to ensure durability and performance.
Performance Characteristics: Impulse turbines exhibit specific performance characteristics that make them suitable for certain applications.
- Efficiency: Impulse turbines are highly efficient at converting kinetic energy into mechanical energy. However, their efficiency can vary depending on load conditions and steam parameters.
- Load Response: Impulse turbines have a quick load response, making them ideal for applications where power demand fluctuates rapidly.
Applications: Impulse turbines are commonly used in industries requiring rapid and efficient power generation, such as in peak-load power plants and certain industrial applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages: High efficiency, quick load response, and robust construction.
- Disadvantages: They may not be as efficient at lower loads and are typically more complex in design than reaction turbines.
4. Reaction Steam Turbines
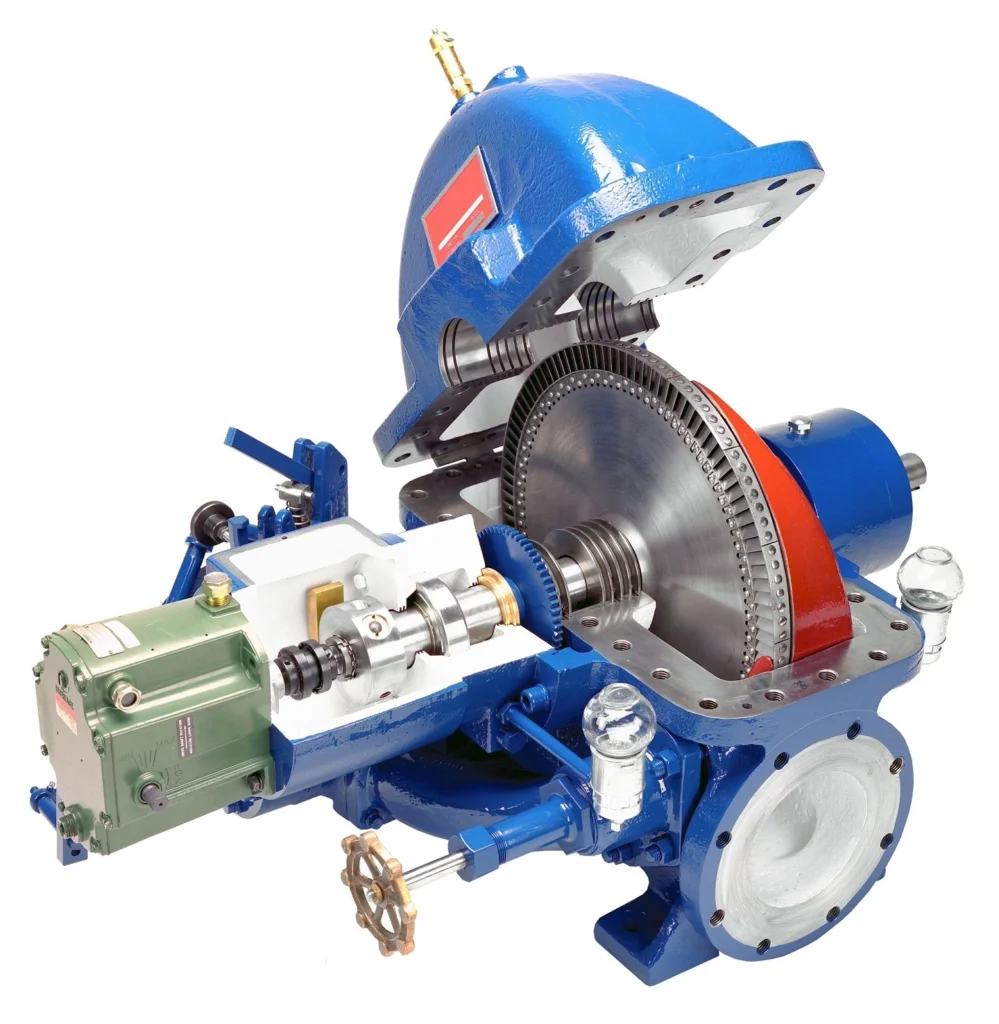

Definition and Working Principle: Reaction turbines operate on the principle of the reaction force generated by the acceleration of steam as it passes through the moving blades. Unlike impulse turbines, where steam is expanded in nozzles, in reaction turbines, steam expands continuously as it flows through both stationary and moving blades.
- Expansion of Steam in Moving Blades: In a reaction turbine, steam expands within the moving blades, generating a reactive force that causes the blades to rotate. The energy conversion process occurs in both the stationary and moving blades.
- Energy Transfer Process: The energy transfer in a reaction turbine is a combination of pressure and velocity changes, with steam expanding and accelerating as it moves through the turbine stages.
Design and Construction: The design of reaction turbines differs from impulse turbines, with a focus on continuous expansion and energy transfer.
- Blade Profiles: Reaction turbine blades are designed to allow steam expansion and to facilitate efficient energy transfer. The blade profiles are often more complex, with a focus on maximizing pressure drop across each stage.
- Pressure and Velocity Changes: As steam passes through the turbine, it undergoes continuous pressure and velocity changes, which are harnessed to produce rotational energy.
- Stator and Rotor Arrangement: The arrangement of stator (stationary blades) and rotor (moving blades) in a reaction turbine is designed to allow for continuous expansion and acceleration of steam, ensuring efficient energy extraction.
Performance Characteristics: Reaction turbines are characterized by their smooth operation and ability to handle varying load conditions effectively.
- Efficiency: Reaction turbines tend to have high efficiency across a wider range of load conditions compared to impulse turbines, making them suitable for base-load power generation.
- Load Response: While reaction turbines are slower to respond to rapid load changes, they excel in applications where consistent power output is required.
Applications: Reaction turbines are widely used in power plants, especially in large-scale base-load generation, where their efficiency and reliability are paramount.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages: High efficiency across a range of conditions, smoother operation, and suitability for large-scale power generation.
- Disadvantages: More complex design, requiring precise manufacturing and higher maintenance.
5. Comparative Analysis of Impulse and Reaction Turbines
Structural Differences: Impulse turbines have distinct nozzles and blades, with energy conversion occurring in the nozzles, while reaction turbines integrate energy conversion throughout the blade stages.
Operational Differences: Impulse turbines excel in situations requiring rapid load changes, while reaction turbines are better suited for steady, continuous operation.
Performance Comparison:
- Efficiency at Different Load Conditions: Reaction turbines generally maintain higher efficiency across a broader range of loads, whereas impulse turbines peak in efficiency under specific conditions.
- Maintenance Requirements: Impulse turbines often have simpler maintenance due to fewer moving parts and less complex blade designs. Reaction turbines, with their more intricate blade profiles and continuous expansion process, may require more frequent maintenance and precision engineering.
- Suitability for Various Power Plants: Impulse turbines are favored in applications with fluctuating power demands, such as peaking power plants, while reaction turbines are preferred in base-load power plants due to their efficiency and reliability.
Cost Analysis:
- Initial Costs: Reaction turbines may have higher initial costs due to more complex design and manufacturing requirements.
- Operating Costs: Operating costs can vary based on maintenance needs, with reaction turbines potentially incurring higher costs due to more frequent and detailed upkeep.
6. Advancements and Innovations in Steam Turbine Technology
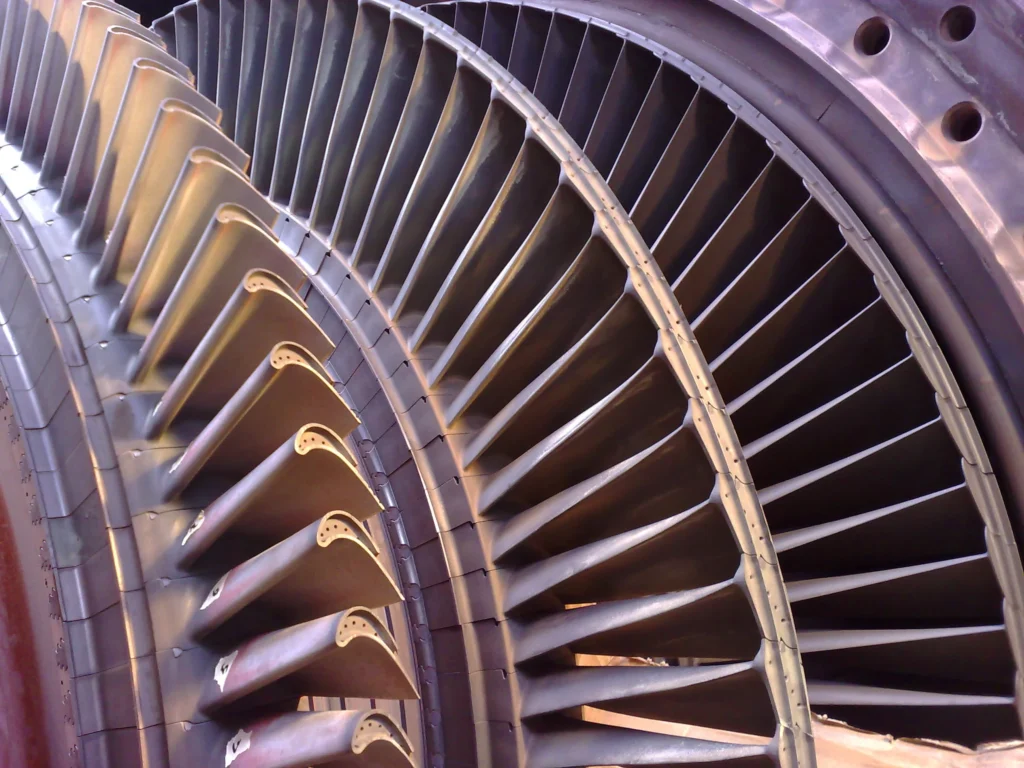
Recent Technological Developments: The steam turbine industry has seen significant advancements, particularly in materials science, blade design, and thermal efficiency. Innovations in blade cooling, high-temperature alloys, and coatings have allowed turbines to operate at higher temperatures and pressures, increasing overall efficiency.
Trends in Turbine Efficiency Improvement: Current trends focus on enhancing efficiency through improved blade aerodynamics, reduced leakage, and advanced monitoring systems that optimize turbine operation in real-time.
Future Prospects:
- Hybrid Designs: Combining features of impulse and reaction turbines to harness the advantages of both, hybrid designs are being explored to create more versatile and efficient turbines.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Sources: Steam turbines are also being adapted for integration with renewable energy sources like concentrated solar power (CSP), where they can operate efficiently under variable thermal conditions.
7. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points: Impulse and reaction steam turbines each have unique characteristics, making them suitable for different applications within the power generation industry. Impulse turbines are ideal for rapid load changes, while reaction turbines excel in steady, continuous operation.
Importance in Modern Energy Systems: As the demand for reliable and efficient power generation continues to grow, steam turbines remain a cornerstone of the energy industry, with ongoing advancements ensuring their relevance for the future.
Final Thoughts: Understanding the differences between impulse and reaction turbines is crucial for selecting the right technology for specific applications. As technology evolves, these turbines will continue to play a vital role in meeting global energy needs.
Sure! Let’s dive into the detailed content for each section. Given the extensive nature of this text, I’ll proceed in segments, providing content for a few sections at a time. This approach allows for a thorough and cohesive development of the text.
1. Introduction
Overview of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines are mechanical devices that convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy through the rotational movement of a shaft. This mechanical energy is then typically converted into electrical energy by coupling the turbine to an electrical generator. Steam turbines are a cornerstone of modern power generation, used extensively in both fossil-fuel and nuclear power plants. They are also found in industrial applications, such as chemical processing plants, where they drive mechanical equipment.
The basic operation of a steam turbine involves steam produced in a boiler being superheated and directed onto the turbine blades. The interaction between the high-pressure steam and the blades causes the turbine shaft to rotate, thus converting the thermal energy of the steam into useful mechanical work. The efficiency and reliability of steam turbines make them a crucial technology in the production of electricity.
Importance in Power Generation: Steam turbines play a vital role in the global energy infrastructure. They are responsible for producing a significant portion of the world’s electricity, particularly in countries that rely heavily on coal, natural gas, or nuclear energy. The efficiency of steam turbines directly impacts the overall efficiency of power plants, influencing both the economic and environmental aspects of energy production.
In addition to their widespread use in large-scale power generation, steam turbines are also utilized in cogeneration systems, where they produce both electricity and useful heat for industrial processes. This dual functionality enhances the overall energy efficiency of these systems, making steam turbines an essential component of modern energy solutions.
Purpose of the Document: The purpose of this document is to provide a comprehensive examination of Impulse and Reaction Steam Turbines. These two types of turbines are the most commonly used in power generation and industrial applications. The document will explore their working principles, design and construction, performance characteristics, applications, and comparative advantages and disadvantages.
By offering an in-depth analysis, this document aims to educate engineers, technical professionals, and students about the critical role of these turbines in the energy sector. It will also provide insights into recent advancements and innovations in turbine technology, highlighting the ongoing evolution of these vital machines.
2. Fundamentals of Steam Turbines
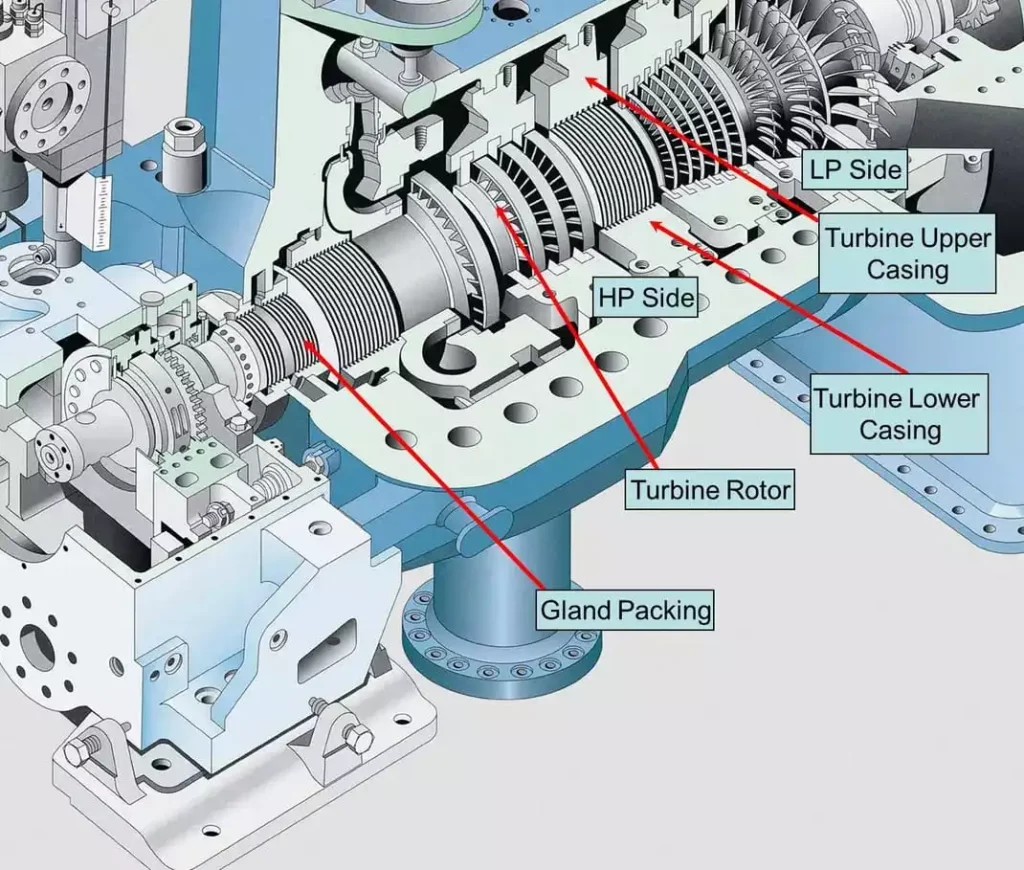
Basic Principles of Steam Turbines: At the core of a steam turbine’s operation is the conversion of thermal energy into mechanical work. This process begins with water being heated in a boiler to produce steam. The steam, under high pressure and temperature, is directed onto the turbine’s blades, which are mounted on a rotor. As the steam flows over these blades, it causes the rotor to spin, generating mechanical energy.
The process of energy conversion in a steam turbine can be broken down into several stages:
- Steam Generation: High-pressure steam is generated in a boiler.
- Expansion: The steam expands through the turbine, losing pressure and temperature but gaining speed as it passes through the turbine blades.
- Mechanical Work: The high-speed steam imparts kinetic energy to the turbine blades, causing the rotor to spin.
- Exhaust: After passing through the turbine, the steam is exhausted at a lower pressure and temperature, often directed into a condenser for reuse in a closed-loop system.
Historical Development: The development of steam turbines has a rich history that traces back to the late 19th century. The first practical steam turbine was invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884. His design, which was a reaction turbine, laid the groundwork for modern steam turbine technology. Around the same time, Gustaf de Laval developed the impulse turbine, which used a different principle of energy conversion but also proved to be highly effective.
Over the years, steam turbines have undergone significant advancements. Early turbines were relatively simple, with low efficiency and limited capacity. However, with the advent of new materials, improved manufacturing techniques, and advanced thermodynamic principles, modern steam turbines have become highly efficient and capable of generating hundreds of megawatts of power.
Types of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines can be broadly classified into two main types based on the method of energy conversion: Impulse Turbines and Reaction Turbines. These two types represent different approaches to extracting energy from steam and have distinct design and operational characteristics.
- Impulse Turbines: In impulse turbines, steam is expanded entirely in nozzles before it reaches the turbine blades. The high-velocity steam jets then strike the blades, imparting momentum and causing the rotor to spin.
- Reaction Turbines: In reaction turbines, steam expands gradually as it flows through both the stationary and moving blades. The continuous expansion within the turbine creates a reaction force that drives the rotor.
Each type has its advantages and is suited to specific applications depending on factors like efficiency, load response, and operational requirements.
Overview of Impulse and Reaction Turbines: Impulse turbines are characterized by their use of high-speed steam jets that strike turbine blades to generate rotational motion. The blades in an impulse turbine are shaped to efficiently capture the kinetic energy of the steam. Reaction turbines, on the other hand, rely on the expansion of steam within the blades themselves, where the pressure drop across the blades creates the reaction force that drives the turbine.
The primary difference between these two types lies in where and how the steam expands. In impulse turbines, steam expansion occurs entirely in the nozzles, while in reaction turbines, steam expansion happens within the blades. This fundamental distinction affects the design, operation, and application of each turbine type.
3. Impulse Steam Turbines

Definition and Working Principle: Impulse steam turbines are a type of turbine where the entire pressure drop of the steam occurs in the stationary nozzles. The steam enters the nozzles at high pressure and is expanded to a lower pressure, converting the steam’s pressure energy into kinetic energy. This high-speed jet of steam is then directed onto the turbine blades, causing them to rotate.
The fundamental principle behind impulse turbines is Newton’s Third Law of Motion, which states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In this case, the action is the high-velocity steam jet striking the blades, and the reaction is the force that causes the blades (and thus the rotor) to spin.
- Newton’s Third Law of Motion: This law underpins the operation of impulse turbines. When the steam exits the nozzle at high velocity, it exerts a force on the turbine blades. The blades, in turn, exert an equal and opposite force on the steam, causing the rotor to rotate.
- Energy Conversion Process: The energy conversion in an impulse turbine is straightforward. Steam is expanded in the nozzles, converting pressure energy into kinetic energy. The high-speed steam jets then impact the turbine blades, transferring kinetic energy to the rotor, which is used to generate mechanical work.
Design and Construction: The design of an impulse turbine is centered around maximizing the efficiency of energy transfer from the steam to the rotor. Key components include nozzles, turbine blades, the rotor, and the stator.
- Blades and Nozzles: The nozzles in an impulse turbine are designed to accelerate the steam to very high speeds. The blades, typically mounted on the rotor, are shaped to capture this kinetic energy effectively. The angle and curvature of the blades are optimized to ensure that the steam imparts maximum force to the rotor.
- Rotor and Stator Arrangement: The rotor carries the moving blades, while the stator holds the stationary nozzles. The alignment of the nozzles and blades is critical for efficient energy transfer. The rotor’s rotation drives the generator to produce electricity.
- Material Considerations: The materials used in impulse turbines must withstand high temperatures and pressures. High-strength steel alloys are commonly used for the rotor and blades, often coated with materials that resist corrosion and wear.
Performance Characteristics: Impulse turbines are known for their specific performance characteristics, which make them suitable for particular applications.
- Efficiency: Impulse turbines are highly efficient at converting kinetic energy into mechanical energy, especially under conditions where the steam pressure is high and the load is constant.
- Load Response: One of the key advantages of impulse turbines is their quick response to changes in load. This makes them ideal for applications where power demand fluctuates, such as in peaking power plants.
Applications: Impulse turbines are widely used in various industrial applications and power generation scenarios, particularly where high efficiency and quick load response are required. They are commonly found in:
- Peak-Load Power Plants: Where the ability to quickly adjust to changing demand is crucial.
- Marine Propulsion: Due to their efficiency and ability to handle fluctuating load conditions.
- Industrial Drive Systems: For applications requiring direct mechanical power from the turbine.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages:
- High efficiency at specific load conditions.
- Quick load response and adaptability to changing power demands.
- Relatively simple maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
- Disadvantages:
- Efficiency can drop significantly at lower loads.
- More complex design in terms of nozzle and blade alignment compared to reaction turbines.
4. Reaction Steam Turbines
Definition and Working Principle: Reaction steam turbines operate on a different principle from impulse turbines. In a reaction turbine, steam expands continuously as it flows through the moving blades. This continuous expansion causes a reaction force that drives the rotor. Unlike impulse turbines, where the steam’s pressure drop occurs entirely in the nozzles, in reaction turbines, the pressure drop occurs across both the stationary and moving blades.
The fundamental operating principle of a reaction turbine is based on the reactive force generated by the steam as it accelerates and expands within the moving blades. This reaction force creates the torque needed to rotate the rotor, driving the connected generator to produce electricity.
- Expansion of Steam in Moving Blades: In a reaction turbine, the steam enters the turbine at high pressure and expands as it passes through the moving blades. The steam’s pressure and velocity decrease as it imparts energy to the blades, causing the rotor to spin.
- Energy Transfer Process: The energy transfer in a reaction turbine involves both pressure and velocity changes. As steam flows through the turbine, it undergoes continuous expansion, converting its thermal energy into mechanical work in a smooth and efficient process.
Design and Construction: The design of a reaction turbine is more complex than that of an impulse turbine due to the continuous expansion process. Key design elements include blade profiles, the arrangement of stationary and moving blades, and materials capable of withstanding the operational stresses.
- Blade Profiles: The blades in a reaction turbine are designed to allow for the smooth expansion of steam, with profiles that optimize the pressure drop across each stage. The shape and angle of the blades are critical for ensuring efficient energy transfer.
- Pressure and Velocity Changes: As steam flows through the turbine, it experiences continuous changes in pressure and velocity. The design must accommodate these changes to ensure that the maximum amount of energy is extracted from the steam.
- Stator and Rotor Arrangement: The stator holds the stationary blades, while the rotor carries the moving blades. The precise alignment of these components is essential for maintaining the efficiency of the turbine. The rotor’s rotation is driven by the reactive force generated as steam expands within the moving blades.
Performance Characteristics: Reaction turbines are known for their smooth operation and ability to maintain high efficiency across a range of load conditions.
- Efficiency: Reaction turbines tend to have higher efficiency across a broader range of load conditions compared to impulse turbines. This makes them particularly suitable for base-load power generation, where steady and continuous operation is required.
- Load Response: Reaction turbines are slower to respond to rapid load changes compared to impulse turbines. However, they are highly reliable in maintaining consistent power output, making them ideal for applications where a stable power supply is critical.
Applications: Reaction turbines are widely used in large-scale power generation, particularly in base-load power plants where efficiency and reliability are paramount. Common applications include:
- Nuclear Power Plants: Where steady, continuous power generation is essential.
- Combined Cycle Power Plants: Where the efficiency of the turbine is crucial for overall plant performance.
- Industrial Cogeneration: Where both electricity and process heat are produced from the same energy source.
Advantages and Disadvantages:
- Advantages:
- High efficiency across a wide range of load conditions.
- Smooth and stable operation, making them ideal for base-load power generation.
- Lower operating noise levels due to the continuous expansion process.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex design and construction compared to impulse turbines.
- Slower response to rapid load changes, which may limit their use in peaking applications.
- Higher maintenance requirements due to the intricate blade design and continuous steam expansion.
5. Comparative Analysis of Impulse and Reaction Turbines
Structural Differences: The structural differences between impulse and reaction turbines stem primarily from their fundamental design principles and how they convert the energy of steam into mechanical work.
- Impulse Turbines: In an impulse turbine, the steam is expanded and accelerated through nozzles, converting its pressure energy into kinetic energy. The turbine blades are typically bucket-shaped and mounted on the rotor. Since the steam expansion occurs entirely in the nozzles, the turbine blades themselves do not experience a significant pressure drop. The rotor design is generally simpler, as it primarily needs to capture the high-velocity steam jets and convert their kinetic energy into rotational motion. The absence of continuous pressure changes within the turbine stages allows for a robust and straightforward design.
- Reaction Turbines: Reaction turbines, on the other hand, feature a more complex structure due to the continuous steam expansion that occurs across both the stationary and moving blades. The blades in a reaction turbine are designed to act as nozzles, where steam is allowed to expand and accelerate. This design requires the rotor to accommodate a continuous change in pressure and velocity across multiple stages. Consequently, the rotor and blade design in a reaction turbine are more intricate, with the blades often designed with varying profiles to handle the gradual expansion and energy extraction process. The overall structure of a reaction turbine is typically more elongated to allow for multiple stages of energy conversion.
Operational Differences: The operational differences between impulse and reaction turbines are closely related to their structural designs and how they handle the energy conversion process.
- Impulse Turbines: Impulse turbines are characterized by their ability to operate efficiently under high-pressure conditions and at specific load levels. They are highly responsive to changes in load, making them suitable for applications where power demand fluctuates frequently. The quick load response of impulse turbines is due to their simpler design and the fact that the energy conversion is localized within the nozzles, allowing for rapid adjustments to steam flow.
- Reaction Turbines: Reaction turbines operate more smoothly and efficiently over a broader range of loads. Their design allows for a continuous expansion of steam, which results in stable and consistent operation. This makes reaction turbines ideal for base-load power generation, where steady, uninterrupted power supply is required. However, their load response is slower compared to impulse turbines, due to the complexity of the energy conversion process that takes place across multiple stages.
Performance Comparison: Performance differences between impulse and reaction turbines are evident in their efficiency, load handling, maintenance requirements, and suitability for various applications.
- Efficiency at Different Load Conditions: Reaction turbines generally exhibit higher efficiency across a wider range of load conditions. This is because the continuous expansion of steam within the turbine stages allows for more complete energy extraction. Impulse turbines, while highly efficient at specific design points, may see a drop in efficiency when operating outside of those conditions.
- Maintenance Requirements: Maintenance requirements for impulse turbines are typically lower due to their simpler design. With fewer moving parts and a less complex energy conversion process, impulse turbines are easier to maintain and generally have lower downtime. Reaction turbines, with their intricate blade designs and continuous expansion process, require more detailed and frequent maintenance. The precision required in manufacturing and maintaining the blades adds to the complexity and cost of upkeep.
- Suitability for Various Power Plants: Impulse turbines are often used in peak-load power plants, where the ability to quickly adjust to changing demand is essential. They are also favored in applications like marine propulsion, where rapid response to varying load conditions is critical. Reaction turbines, on the other hand, are well-suited for base-load power plants, such as those in nuclear or combined cycle facilities, where their efficiency and reliability under continuous operation are highly valued.
Cost Analysis: Cost considerations play a significant role in the selection between impulse and reaction turbines, particularly in terms of initial investment and ongoing operating costs.
- Initial Costs: The initial cost of installing a reaction turbine is generally higher than that of an impulse turbine. This is due to the more complex design, the need for precision engineering, and the larger physical size required to accommodate the multiple stages of energy conversion. The materials used in reaction turbines must also be of higher quality to withstand the continuous pressure and velocity changes, further adding to the cost.
- Operating Costs: Operating costs for reaction turbines can also be higher due to the increased maintenance requirements and the need for periodic inspection and blade replacement. However, these costs can be offset by the higher efficiency and better performance of reaction turbines in certain applications. Impulse turbines, with their simpler design and lower maintenance needs, generally have lower operating costs, making them more economical in applications where high efficiency is not the primary concern.
6. Advancements and Innovations in Steam Turbine Technology
Recent Technological Developments: The field of steam turbine technology has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by the need for higher efficiency, greater reliability, and reduced environmental impact. Innovations have been particularly notable in the areas of materials science, aerodynamic design, and digital monitoring.
- Materials Science: Advances in materials science have led to the development of high-temperature alloys and coatings that allow steam turbines to operate at higher temperatures and pressures. These materials not only enhance the efficiency of the turbines but also increase their longevity by improving resistance to wear and corrosion. Ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) and superalloys are examples of materials that are increasingly used in turbine blades and other critical components.
- Aerodynamic Design: Improvements in aerodynamic design have focused on optimizing the shape and configuration of turbine blades to reduce aerodynamic losses and increase efficiency. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling has become a key tool in the design process, allowing engineers to simulate and refine turbine performance under various operating conditions. The development of advanced blade cooling techniques, such as internal cooling channels and thermal barrier coatings, has also contributed to better performance at higher temperatures.
- Digital Monitoring and Control: The integration of digital monitoring and control systems has revolutionized the operation of steam turbines. Real-time data collection and analysis allow for precise control of turbine performance, enabling operators to optimize efficiency and detect potential issues before they lead to failures. Predictive maintenance systems, powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, are increasingly being used to schedule maintenance activities based on actual operating conditions rather than fixed intervals, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Trends in Turbine Efficiency Improvement: The pursuit of higher efficiency is a driving force behind many of the innovations in steam turbine technology. Several trends are emerging as key contributors to efficiency improvements.
- Higher Operating Temperatures: Increasing the operating temperature of steam turbines is one of the most effective ways to improve efficiency. Advanced materials and cooling techniques are enabling turbines to operate at temperatures exceeding 600°C, pushing the boundaries of what was previously possible.
- Reduced Leakage: Minimizing steam leakage within the turbine is another critical area of focus. Sealing technologies, such as brush seals and abradable coatings, are being developed to reduce leakage between the rotating and stationary components of the turbine, thereby improving overall efficiency.
- Hybrid Designs: The combination of impulse and reaction turbine principles in hybrid designs is being explored to harness the strengths of both types. These hybrid turbines aim to achieve higher efficiency and flexibility across a broader range of operating conditions, making them suitable for a variety of power generation applications.
Future Prospects: Looking ahead, the future of steam turbine technology is likely to be shaped by several emerging trends and developments.
- Hybrid Designs: As mentioned, hybrid turbine designs that incorporate both impulse and reaction stages are gaining traction. These designs offer the potential for greater efficiency and operational flexibility, making them ideal for use in power plants that must accommodate varying load demands and integrate with other energy sources.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Sources: The role of steam turbines is also evolving in the context of the transition to renewable energy. Steam turbines are being adapted for use in conjunction with renewable energy sources such as concentrated solar power (CSP) and geothermal energy. In these applications, steam turbines must operate efficiently under variable thermal conditions, which presents both challenges and opportunities for innovation.
- Digital Twin Technology: The adoption of digital twin technology is expected to grow, providing operators with a virtual replica of the steam turbine that can be used to simulate and optimize performance. This technology allows for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and the identification of potential improvements, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational risks.
7. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points: Impulse and reaction steam turbines represent two fundamental approaches to the conversion of thermal energy into mechanical work. Each type has distinct structural, operational, and performance characteristics that make them suitable for different applications within the power generation industry. Impulse turbines are known for their quick load response and simpler design, making them ideal for applications with fluctuating power demands. In contrast, reaction turbines excel in efficiency and stability, making them the preferred choice for base-load power generation.
The continuous advancements in steam turbine technology, including improvements in materials, aerodynamic design, and digital control systems, are pushing the boundaries of efficiency and performance. These innovations are helping to ensure that steam turbines remain a critical component of modern energy systems, even as the energy landscape evolves toward more sustainable and renewable sources.
Importance in Modern Energy Systems: Steam turbines continue to play a crucial role in global energy production, particularly in large-scale power plants that require reliable and efficient electricity generation. As the demand for energy grows and the focus on reducing carbon emissions intensifies, the efficiency and adaptability of steam turbines will be increasingly important. The ability of steam turbines to integrate with renewable energy sources and operate efficiently under varying conditions positions them as a key technology in the transition to a more sustainable energy future.
Final Thoughts: Understanding the differences between impulse and reaction turbines is essential for engineers, operators, and decision-makers in the energy sector. By selecting the appropriate turbine type for specific applications, it is possible to optimize performance, reduce costs, and meet the evolving demands of the energy industry. As technological advancements continue to enhance the capabilities of steam turbines, they will remain a vital part of the global energy infrastructure, contributing to the reliable and efficient generation of power for decades to come.
- Introduction: Provided an overview of steam turbines, their importance in power generation, and the purpose of the document.
- Fundamentals of Steam Turbines: Discussed the basic principles, historical development, and the classification of steam turbines into impulse and reaction types.
- Impulse Steam Turbines: Detailed the working principle, design, construction, performance characteristics, applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of impulse turbines.
- Reaction Steam Turbines: Covered the working principle, design, construction, performance characteristics, applications, and the advantages and disadvantages of reaction turbines.
- Comparative Analysis: Analyzed the structural and operational differences, performance, and cost implications between impulse and reaction turbines.
- Advancements and Innovations: Highlighted recent technological developments, trends in efficiency improvements, and future prospects in steam turbine technology.
- Conclusion: Summarized the key points, emphasized the importance of steam turbines in modern energy systems, and provided final thoughts on their future role.
Steam turbines are pivotal components in modern power generation, converting thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical energy and subsequently into electricity. This document presents an in-depth examination of the two primary types of steam turbines: Impulse and Reaction turbines.
The Impulse Turbine operates on the principle where high-pressure steam is expanded entirely through nozzles before impinging on the turbine blades, converting pressure energy into kinetic energy. Characterized by their bucket-shaped blades and simpler design, impulse turbines offer quick load response, making them ideal for applications with fluctuating power demands, such as peak-load power plants and marine propulsion systems. However, their efficiency can diminish under variable load conditions.
In contrast, the Reaction Turbine facilitates continuous steam expansion across both stationary and moving blades, generating a reactive force that propels the rotor. With intricate blade designs and elongated structures to accommodate multiple expansion stages, reaction turbines excel in efficiency and stability, rendering them suitable for base-load power generation in nuclear and combined cycle power plants. Their complex design, however, entails higher initial and maintenance costs.
A comparative analysis reveals that while impulse turbines are advantageous for their responsiveness and maintenance simplicity, reaction turbines offer superior efficiency across diverse load conditions. Advancements in materials science, aerodynamic design, and digital monitoring have further enhanced the performance and reliability of both turbine types. Notably, the integration of high-temperature alloys, computational fluid dynamics (CFD) in blade design, and predictive maintenance systems underscore the technological evolution in this domain.
Looking forward, hybrid turbine designs amalgamating impulse and reaction principles, integration with renewable energy systems like concentrated solar power (CSP), and the adoption of digital twin technologies are poised to redefine steam turbine applications. Understanding the nuanced differences between impulse and reaction turbines is imperative for optimizing their deployment in alignment with specific energy generation requirements.
Given the detailed nature of the content already provided, I will now expand on how this document could be utilized effectively, including suggestions for visual aids, references, and how the content might be structured on a formal website. Additionally, I will offer ideas for extending the discussion into related areas, such as turbine maintenance practices or case studies of specific turbine applications.
Visual Aids and Supplementary Materials
1. Diagrams and Illustrations:
- Impulse Turbine Diagram: A labeled diagram showing the flow of steam through the nozzles and onto the blades, highlighting the energy conversion process.
- Reaction Turbine Diagram: A detailed illustration showing the continuous expansion of steam across multiple blade stages, emphasizing the difference in pressure and velocity changes.
- Comparative Flowchart: A side-by-side comparison chart of impulse and reaction turbines, visually displaying their structural and operational differences.
- Efficiency Curves: Graphs comparing the efficiency of impulse and reaction turbines under various load conditions.
- Material Composition Chart: A chart showing the materials used in different turbine components, with a focus on high-temperature alloys and coatings.
2. Case Studies:
- Case Study 1: Impulse Turbines in Peak-Load Power Plants: An example of how impulse turbines are used in a specific power plant, including operational data and performance metrics.
- Case Study 2: Reaction Turbines in Nuclear Power Plants: A detailed case study of a nuclear power plant that utilizes reaction turbines, showcasing the efficiency and reliability of the system.
3. Interactive Content:
- 3D Models: Interactive 3D models of impulse and reaction turbines that allow users to explore different components and see how they function in real-time.
- Video Explainers: Short videos that visually explain the working principles of both turbine types, using animations to illustrate key concepts.
References and Further Reading
To strengthen the credibility and depth of the document, it’s advisable to include references to authoritative sources, such as:
- Textbooks and Handbooks:
- “Steam Turbines: Design, Application, and Re-Rating” by Heinz P. Bloch and Murari Singh.
- “Turbomachinery: Design and Theory” by Rama S.R. Gorla and Aijaz A. Khan.
- Technical Papers:
- Papers published in journals like the ASME Journal of Turbomachinery or Energy Conversion and Management that discuss advances in steam turbine technology.
- Industry Reports:
- Reports from organizations like the International Energy Agency (IEA) or the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) that provide insights into trends and innovations in turbine technology.
Website Structure and Content Placement
When structuring this content for a formal website, it’s essential to organize the information in a user-friendly and accessible manner. Here’s a suggested structure:
1. Homepage:
- Introduction to Steam Turbines: A brief overview with links to detailed sections on impulse and reaction turbines.
- Featured Innovations: Highlight the latest advancements and trends in steam turbine technology.
2. Detailed Sections:
- Impulse Steam Turbines:
- Working Principles
- Design and Construction
- Performance Characteristics
- Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Reaction Steam Turbines:
- Working Principles
- Design and Construction
- Performance Characteristics
- Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages
- Comparative Analysis:
- Structural and Operational Differences
- Performance and Cost Comparison
- Technological Advancements:
- Recent Innovations
- Future Prospects in Turbine Technology
3. Supplementary Content:
- Case Studies and Applications: Real-world examples showcasing the use of impulse and reaction turbines.
- Interactive Tools: 3D models, video explainers, and efficiency calculators.
4. Resources and References:
- Further Reading: Links to books, papers, and industry reports.
- Glossary: Definitions of key technical terms used in the document.
5. Blog or News Section:
- Latest Research: Articles on the newest research in turbine technology.
- Industry News: Updates on developments in the power generation sector.
Extended Discussion Topics
To expand the content further, consider including additional sections that explore related topics, such as:
1. Turbine Maintenance Practices:
- Preventive Maintenance: Best practices for maintaining impulse and reaction turbines to maximize efficiency and longevity.
- Predictive Maintenance: The role of AI and machine learning in predicting turbine maintenance needs.
2. Environmental Impact and Efficiency:
- Reducing Emissions: How advancements in turbine technology contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Efficiency in Renewable Energy Integration: The role of steam turbines in enhancing the efficiency of renewable energy systems like CSP and geothermal power.
3. Historical Evolution of Turbines:
- Milestones in Turbine Development: A historical timeline showcasing key innovations and developments in turbine technology.
- Pioneers in Turbine Design: Biographical sketches of inventors and engineers who significantly contributed to turbine technology.
4. Economic Impact of Turbines:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: An analysis of the economic benefits of using advanced steam turbines in power generation.
- Market Trends: A discussion on global market trends for steam turbines, including demand, manufacturing, and export statistics.
By incorporating these elements, the document not only serves as a technical resource but also as a comprehensive guide that provides context, practical insights, and real-world applications. This approach will ensure the content is engaging, informative, and valuable to a broad audience, from engineers and industry professionals to students and educators.
Micro steam turbines
Micro steam turbines are smaller-scale versions of traditional steam turbines, designed for lower power outputs, typically ranging from a few kilowatts to several megawatts. They are gaining popularity in various applications due to their ability to efficiently generate power from low-grade heat sources, provide decentralized energy solutions, and integrate with renewable energy systems. Below is an in-depth exploration of micro steam turbines.
1. Introduction to Micro Steam Turbines
Definition and Scope: Micro steam turbines are compact, efficient devices that convert thermal energy from steam into mechanical work, which is then used to generate electricity. Unlike large-scale steam turbines used in central power plants, micro steam turbines are designed for distributed power generation, small-scale industrial applications, and renewable energy systems.
Applications: Micro steam turbines are versatile and can be used in a variety of settings, including:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: Micro steam turbines are often integrated into CHP systems, where they generate electricity and utilize waste heat for heating or industrial processes.
- Waste Heat Recovery: They are used to recover energy from industrial processes, such as in refineries, cement plants, and steel mills, where waste heat can be converted into electricity.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Micro steam turbines can be paired with renewable energy sources like biomass, concentrated solar power (CSP), and geothermal energy, providing a reliable and sustainable power generation solution.
- Remote and Off-Grid Power Supply: In remote locations or off-grid areas, micro steam turbines offer a reliable source of electricity, particularly in areas with limited access to traditional power grids.
2. Working Principles and Design of Micro Steam Turbines
Basic Operation: The operation of a micro steam turbine is similar to that of larger turbines but scaled down to accommodate lower power outputs. The process involves:
- Steam Generation: Steam is generated from a boiler or a heat recovery system, typically at lower pressures and temperatures than in large-scale systems.
- Energy Conversion: The steam is directed onto the turbine blades, causing the rotor to spin. The mechanical energy produced is then converted into electrical energy using a generator.
- Exhaust: After passing through the turbine, the steam is condensed or exhausted, and the cycle is repeated.
Design Features: Micro steam turbines are designed to optimize efficiency and reliability at small scales. Key design elements include:
- Compact Blades: The blades are designed to handle lower steam volumes while maximizing energy extraction. The smaller size requires precise manufacturing to ensure efficiency.
- Modular Design: Many micro steam turbines feature a modular design, allowing for easy integration with other systems and scalability to meet varying power demands.
- Material Selection: Due to the lower operating temperatures and pressures, micro steam turbines can be constructed from less expensive materials, reducing costs while maintaining durability.
Technology Variants:
- Single-Stage vs. Multi-Stage: Micro steam turbines can be single-stage, where the steam passes through one set of blades, or multi-stage, where the steam expands across multiple stages to extract more energy.
- Impulse vs. Reaction: Just like larger turbines, micro steam turbines can operate on impulse or reaction principles, depending on the specific application and efficiency requirements.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Micro Steam Turbines
Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Micro steam turbines are highly efficient in converting heat to electricity, especially in CHP systems where waste heat can be utilized.
- Flexibility: They can be used with a variety of heat sources, including fossil fuels, biomass, solar, and geothermal, making them versatile in different environments.
- Scalability: The modular design allows micro steam turbines to be scaled up or down depending on the power needs, offering flexibility in deployment.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: When integrated with renewable energy sources or waste heat recovery systems, micro steam turbines contribute to lower carbon emissions.
- Decentralized Power Generation: They support decentralized power generation, reducing the dependency on central power plants and enhancing energy security in remote areas.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Power Output: Micro steam turbines are not suitable for applications requiring large-scale power generation, as their output is limited.
- Initial Costs: While smaller than traditional turbines, the initial investment for micro steam turbines can still be significant, particularly in remote installations.
- Maintenance: Though generally low-maintenance, micro steam turbines require regular inspection and upkeep to ensure long-term efficiency and reliability.
- Steam Supply Requirements: The efficiency of micro steam turbines is heavily dependent on the quality and consistency of the steam supply, which may require sophisticated control systems.
4. Applications and Case Studies

Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: Micro steam turbines are widely used in CHP systems to maximize energy efficiency. For example, in a small industrial plant, a micro steam turbine can generate electricity while the waste steam is used for heating, resulting in substantial energy savings.
Waste Heat Recovery: In a steel mill, waste heat from the furnaces can be captured and used to generate steam, which then powers a micro steam turbine to produce electricity. This not only improves the plant’s overall efficiency but also reduces its environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
Renewable Energy Integration: In a biomass plant, micro steam turbines can be employed to generate electricity from steam produced by burning organic waste. This application highlights the ability of micro steam turbines to provide renewable energy solutions in areas with abundant biomass resources.
Remote and Off-Grid Power Supply: In remote communities, micro steam turbines can be paired with small-scale solar thermal systems to provide a consistent and reliable power supply, reducing reliance on diesel generators and improving energy sustainability.
5. Future Trends and Innovations in Micro Steam Turbines
Technological Advancements:
- Improved Efficiency: Ongoing research focuses on enhancing the efficiency of micro steam turbines through better blade design, advanced materials, and optimized steam conditions.
- Integration with Smart Grids: As part of the move toward smart grid technology, micro steam turbines are being integrated with digital control systems that allow for real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and remote operation, improving overall system efficiency and reliability.
- Hybrid Systems: Hybrid systems combining micro steam turbines with other renewable energy technologies, such as solar PV and wind, are emerging as a way to ensure continuous power supply in decentralized and off-grid systems.
Market Growth: The market for micro steam turbines is expected to grow as industries and communities seek more sustainable and efficient energy solutions. The increasing emphasis on energy efficiency, the adoption of renewable energy, and the need for decentralized power generation will drive demand for these compact and versatile turbines.
Environmental Impact: With the global focus on reducing carbon emissions, micro steam turbines will play a critical role in energy systems that prioritize sustainability. Their ability to harness waste heat and integrate with renewable energy sources makes them an attractive option for reducing the environmental footprint of power generation.
6. Conclusion
Summary: Micro steam turbines represent a promising technology for small-scale power generation, offering high efficiency, flexibility, and the ability to integrate with a wide range of heat sources. Their applications in CHP systems, waste heat recovery, renewable energy integration, and remote power supply underscore their versatility and importance in the future energy landscape.
Final Thoughts: As technological advancements continue to improve the performance and reduce the costs of micro steam turbines, their adoption is likely to increase, particularly in industries and regions where decentralized, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions are needed. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of micro steam turbines is essential for engineers, operators, and decision-makers looking to optimize energy systems in a variety of settings.
Steam Turbines
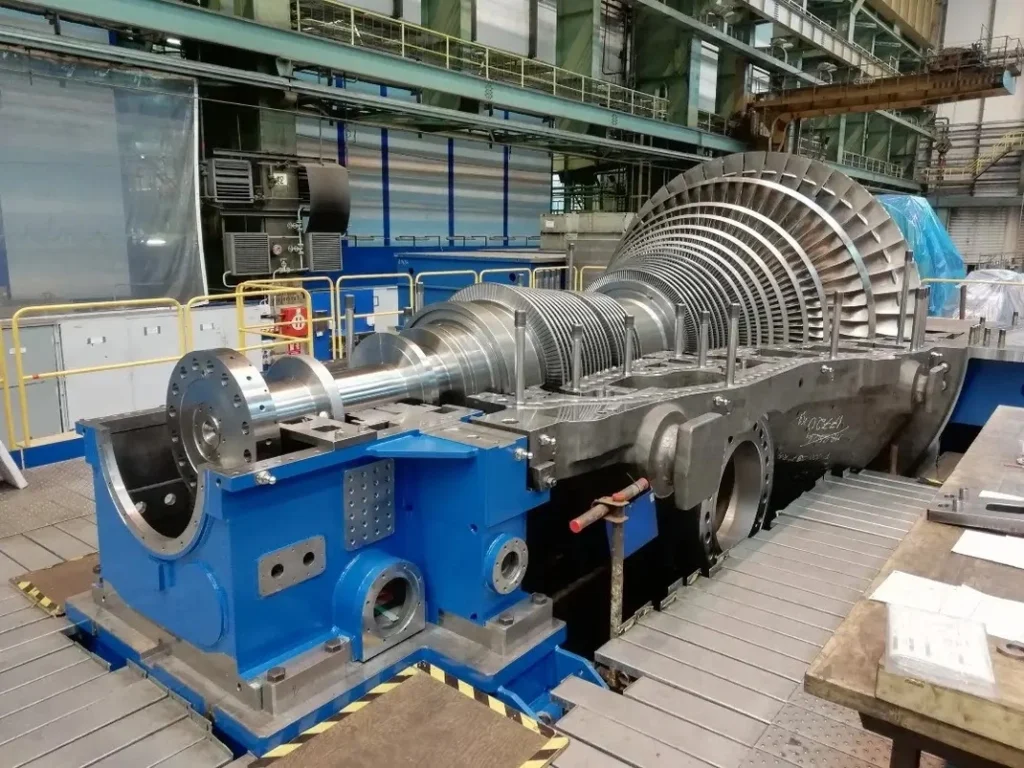
Steam turbines are a fundamental component of modern power generation and various industrial processes. They convert thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy, which can then be used to generate electricity or drive machinery. The concept of harnessing steam power dates back to ancient times, with early attempts to use steam for mechanical purposes seen in the aeolipile, a simple steam-powered device invented by Hero of Alexandria in the 1st century AD. However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that steam turbines, as we know them today, began to take shape.
The breakthrough in steam turbine technology came in the late 19th century with the work of Sir Charles Parsons and Gustaf de Laval. Sir Charles Parsons is often credited with inventing the modern steam turbine in 1884, when he developed a prototype capable of driving an electrical generator. This invention marked a significant leap in efficiency compared to earlier steam engines. Parsons’ steam turbine quickly became the preferred method for generating electricity, and its design principles are still used in modern turbines.
Gustaf de Laval, a Swedish engineer, made significant contributions to the development of steam turbines, particularly in high-speed turbines. His work in the 1880s and 1890s led to the creation of impulse turbines, which use the kinetic energy of steam to drive the turbine blades. These developments laid the foundation for the widespread adoption of steam turbines in various industries.
Importance in Modern Industry
Today, steam turbines play a crucial role in the global energy landscape. They are used in thermal power plants to generate a significant portion of the world’s electricity. In a typical thermal power plant, steam is produced by burning fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, or oil, or by utilizing nuclear energy. The steam is then directed into the turbine, where it expands and drives the turbine blades, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then used to rotate an electrical generator, producing electricity.
Steam turbines are also integral to various industrial processes. They are used in the petrochemical industry to drive compressors and pumps, in the steel industry for mechanical drives, and in the paper industry to generate electricity and drive machinery. Additionally, steam turbines are employed in marine propulsion systems, particularly in large vessels like aircraft carriers and submarines, where their reliability and efficiency are highly valued.
The versatility and efficiency of steam turbines make them indispensable in both traditional and modern energy systems. They are compatible with a wide range of energy sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear power, and renewable sources such as biomass, geothermal, and concentrated solar power. This adaptability ensures that steam turbines will continue to play a vital role in the global energy mix as the world transitions towards more sustainable energy solutions.
Fundamentals of Steam Turbines
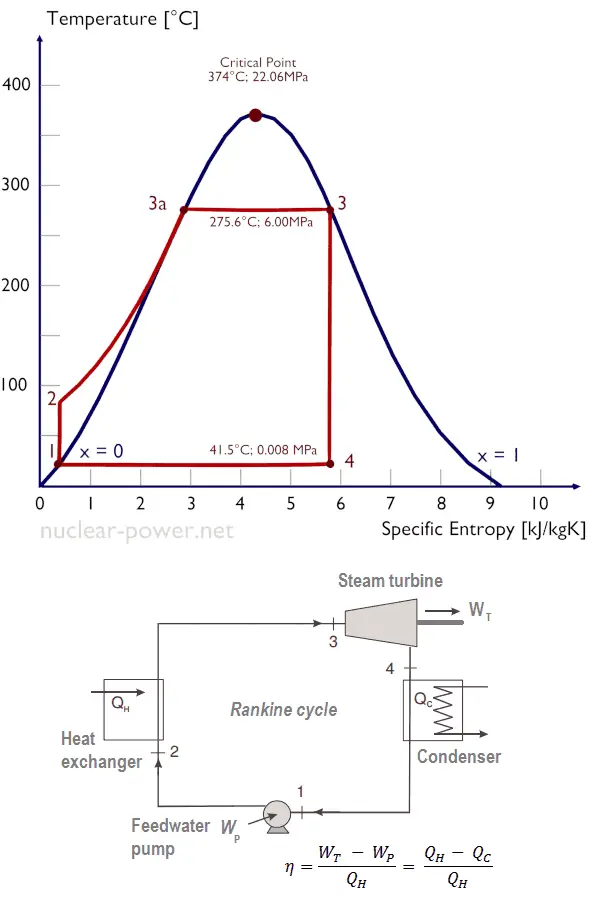
Basic Principles
At the core of a steam turbine’s operation is the conversion of thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy. This process is grounded in the principles of thermodynamics, specifically the Rankine cycle, which is the fundamental thermodynamic cycle used in steam turbine operations.
In simple terms, the Rankine cycle involves four main processes:
- Heat Addition: In a boiler, water is heated at constant pressure, transforming it into steam. This high-pressure steam contains a significant amount of thermal energy.
- Expansion: The high-energy steam is directed into the turbine, where it expands. As the steam expands, its pressure and temperature drop, and it imparts kinetic energy to the turbine blades, causing them to rotate. This rotational energy is then transferred to a shaft connected to an electrical generator or mechanical equipment.
- Condensation: After passing through the turbine, the steam is exhausted into a condenser, where it is cooled and condensed back into water.
- Pumping: The condensed water is then pumped back to the boiler to begin the cycle again.
The efficiency of a steam turbine is determined by how effectively it converts the thermal energy in the steam into mechanical energy. Factors such as steam pressure, temperature, and the design of the turbine blades play crucial roles in determining this efficiency.
Key Components
Steam turbines consist of several critical components, each playing a specific role in the turbine’s operation:
- Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the turbine and consists of a shaft and attached blades. As steam passes through the turbine, it causes the rotor to spin, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy.
- Stator: The stator is the stationary part of the turbine that surrounds the rotor. It contains fixed blades that direct the flow of steam onto the rotor blades in an efficient manner.
- Casing: The casing encases the entire turbine, providing structural support and containing the steam within the turbine. It also protects the internal components from external elements.
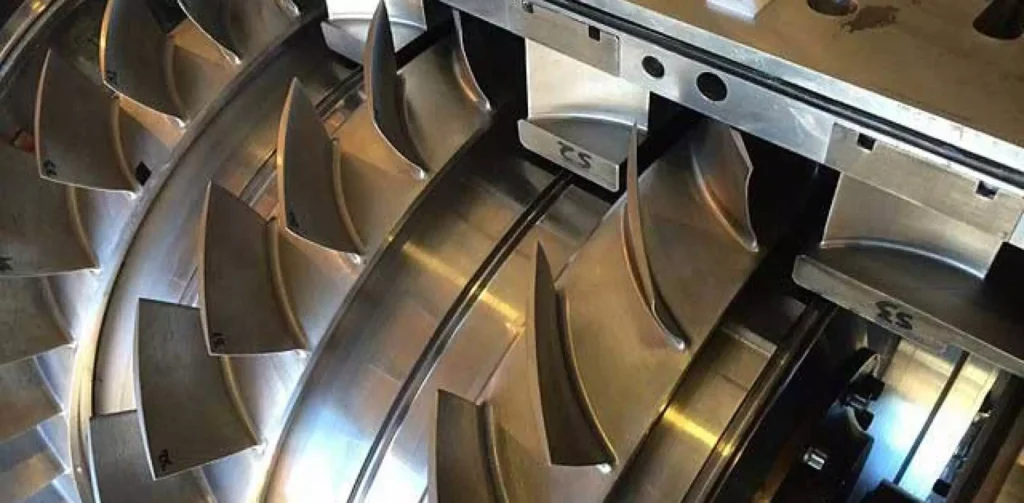
- Blades: The turbine blades are crucial for the conversion of energy. There are two main types of blades: fixed blades (attached to the stator) and moving blades (attached to the rotor). The design and arrangement of these blades are critical for the efficient operation of the turbine.
- Steam Supply System: This system includes the pipes, valves, and other components that deliver steam to the turbine at the required pressure and temperature. It also controls the flow of steam into the turbine.
- Condenser: The condenser cools the exhaust steam from the turbine, converting it back into water to be reused in the cycle. It is typically a heat exchanger that removes the latent heat of vaporization from the steam.
- Governor: The governor is a control mechanism that regulates the turbine’s speed by adjusting the steam flow. It ensures that the turbine operates at the desired speed and can respond to changes in load demand.
Types of Steam Turbines
Steam turbines are classified based on their design, method of steam expansion, and application. The main types include:
- Impulse Turbines: In impulse turbines, high-pressure steam is directed onto the turbine blades through nozzles. The steam jets strike the blades, causing them to move, but the steam pressure remains constant as it passes over the blades. The rotor’s motion is purely due to the impulse force from the steam. Impulse turbines are often used in high-speed applications and are suitable for driving generators in power plants.
- Reaction Turbines: Unlike impulse turbines, reaction turbines utilize both the impulse of steam and the reaction force generated as steam expands and accelerates through the moving blades. The steam pressure drops as it passes through the blades, and this pressure drop is what drives the rotor. Reaction turbines are commonly used in lower-speed applications and are often found in industrial settings.
- Condensing Turbines: These turbines are designed to exhaust steam at a lower pressure, usually into a condenser, where the steam is condensed into water. Condensing turbines are widely used in power generation, where maximum efficiency is required.
- Non-Condensing Turbines: Also known as back-pressure turbines, these turbines exhaust steam at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. The exhaust steam can be used for heating or other industrial processes. Non-condensing turbines are commonly used in cogeneration systems where both electricity and process steam are needed.
- Extraction Turbines: Extraction turbines are designed to extract steam at one or more points along the turbine for industrial processes or heating. The remaining steam continues through the turbine for power generation. These turbines provide flexibility in applications where steam at different pressures is required.
- Reheat Turbines: In reheat turbines, steam is expanded through a high-pressure stage of the turbine, reheated in the boiler, and then expanded further in a lower-pressure stage. Reheating improves the efficiency of the cycle and reduces the moisture content of the steam, which can help to reduce blade erosion.
- Industrial Turbines: These are designed for specific industrial applications, such as driving compressors, pumps, or fans. Industrial turbines can be either impulse or reaction types, depending on the specific application requirements.
- Marine Turbines: Used in naval vessels and large commercial ships, marine turbines are designed to be highly reliable and capable of operating under the challenging conditions at sea. They are typically reaction turbines and are designed to drive propellers or generators for propulsion.
Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics
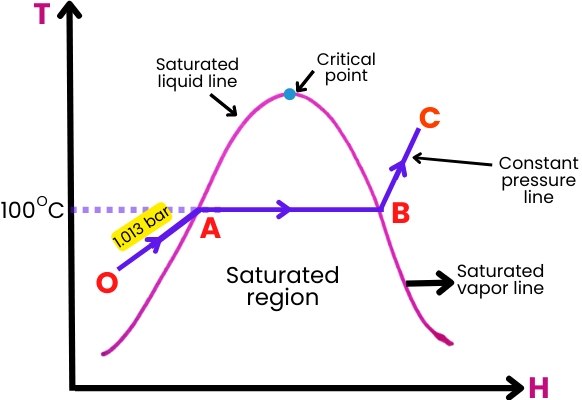
Thermodynamic Cycles
The operation of steam turbines is fundamentally based on thermodynamic cycles, with the Rankine cycle being the most important for understanding how these machines work. The Rankine cycle, named after William John Macquorn Rankine, is a closed-loop cycle that converts heat into work, making it the backbone of steam turbine operations in power plants and industrial settings.
- The Rankine Cycle: The Rankine cycle consists of four main processes:
- Isentropic Compression: The working fluid (water) is pumped from a low pressure to a high pressure. This process requires work input, typically provided by a pump.
- Isobaric Heat Addition: The high-pressure water is heated in a boiler at constant pressure, turning it into high-pressure steam.
- Isentropic Expansion: The high-pressure steam is expanded in the turbine, doing work by turning the turbine’s rotor. As the steam expands, its pressure and temperature drop.
- Isobaric Heat Rejection: The expanded steam is condensed at constant pressure back into water, completing the cycle.
- Reheat Cycle: In a reheat cycle, steam is expanded in a high-pressure turbine, reheated in the boiler, and then expanded again in a low-pressure turbine. This process increases the thermal efficiency of the cycle by allowing the steam to expand through a greater pressure range, reducing the moisture content at the turbine’s exhaust, which in turn minimizes turbine blade erosion.
- Regenerative Cycle: The regenerative cycle improves efficiency by preheating the feedwater entering the boiler using steam extracted from various stages of the turbine. This reduces the amount of fuel needed to heat the water to the desired temperature, thereby improving overall efficiency.
- Combined Cycle: The combined cycle is a modern approach that combines a gas turbine cycle with a steam turbine cycle. The exhaust gases from the gas turbine are used to generate steam in a heat recovery steam generator (HRSG), which then powers a steam turbine. This setup allows for very high overall efficiency, often exceeding 60%.
Fluid Dynamics in Steam Turbines
Fluid dynamics plays a crucial role in the operation of steam turbines, as the efficient conversion of steam energy into mechanical work depends on the controlled flow of steam through the turbine.
- Steam Flow and Velocity Triangles: The flow of steam through a turbine is characterized by velocity triangles, which are geometric representations of the velocity of steam relative to the blades of the turbine. These triangles help in analyzing the energy conversion process as the steam flows through both the stationary (stator) and moving (rotor) blades.
- Absolute Velocity: This is the velocity of the steam relative to the stationary components of the turbine.
- Relative Velocity: This is the velocity of the steam relative to the moving blades of the rotor.
- Blade Velocity: The velocity at which the turbine blades move.
- Impulse and Reaction Principles: Steam turbines operate on either impulse or reaction principles, or a combination of both.
- Impulse Turbines: In impulse turbines, steam is expanded through nozzles, converting its pressure energy into kinetic energy before it hits the rotor blades. The rotor blades are designed to absorb this kinetic energy, causing the rotor to spin.
- Reaction Turbines: In reaction turbines, the steam undergoes a pressure drop as it passes through the rotor blades, which are shaped to act as nozzles. The pressure drop results in a reactive force that turns the rotor. This principle is similar to how a jet engine works.
- Expansion and Losses: As steam expands through the turbine, it loses energy due to several factors, including friction, heat losses, and mechanical losses. These losses reduce the overall efficiency of the turbine. Understanding and minimizing these losses is crucial for optimizing turbine performance.
- Frictional Losses: Occur due to the friction between steam and the turbine blades and internal surfaces.
- Heat Losses: Result from the heat exchange between steam and the turbine casing or the environment.
- Mechanical Losses: Include losses in bearings, seals, and other mechanical components of the turbine.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Heat transfer is a critical aspect of steam turbine operation, influencing both efficiency and performance. The primary heat transfer mechanisms involved are conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat through a solid material, such as the turbine casing or blades. In steam turbines, conduction occurs when heat flows through the metal components from the high-temperature steam to cooler regions. The thermal conductivity of the materials used in turbine construction is an important factor, as it affects the rate of heat transfer and the temperature distribution within the turbine.
- Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat between a solid surface and a fluid, in this case, steam. It occurs when steam flows over the turbine blades and heat is transferred from the steam to the blade material. The efficiency of this process is influenced by factors such as steam velocity, turbulence, and the surface roughness of the blades.
- Forced Convection: In steam turbines, forced convection occurs as steam is forced through the turbine at high velocities. The design of the turbine blades and the flow paths are optimized to enhance heat transfer through forced convection.
- Natural Convection: Natural convection plays a lesser role in steam turbines but can occur in areas where steam or air is stagnant. Managing natural convection is important in turbine cooling and in maintaining structural integrity.
- Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. In steam turbines, radiation heat transfer is typically less significant than conduction and convection but can become important at very high temperatures, such as those found in the superheater sections of a boiler or in high-temperature turbines.
- Thermal Radiation: The turbine components emit thermal radiation based on their temperature. This radiation can contribute to heat losses if not properly managed through insulation and other thermal management techniques.
Design and Manufacturing of Steam Turbines

Design Process
Designing a steam turbine is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, materials science, and mechanical engineering. The primary goals in designing a steam turbine are to maximize efficiency, ensure reliability, and meet the specific operational requirements of the application.
- Thermodynamic Efficiency: The design begins with thermodynamic calculations to determine the optimal operating conditions, such as steam pressure, temperature, and flow rate. Engineers use these calculations to design the turbine stages, ensuring that each stage extracts the maximum possible energy from the steam.
- Blade Design: The design of the turbine blades is crucial for efficiency and reliability. Blades must be aerodynamically optimized to maximize energy extraction while minimizing losses due to friction, turbulence, and separation. The shape, angle, and length of the blades are carefully calculated, often using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations to model the flow of steam through the turbine.
- Material Selection: The materials used in turbine construction must withstand high temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses. Material selection is driven by the need for strength, durability, resistance to corrosion and erosion, and the ability to maintain performance under thermal cycling. Common materials include high-strength alloys, stainless steel, and nickel-based superalloys.
- Cooling and Heat Management: In high-temperature turbines, especially those used in power generation, cooling is a critical design consideration. Blades and other components are often internally cooled using air or steam to prevent overheating and maintain structural integrity. Advanced cooling designs, such as film cooling or transpiration cooling, may be used in particularly demanding applications.
- Rotor Dynamics and Balancing: The rotor is a critical component that must be carefully designed to ensure smooth and reliable operation. Engineers must account for rotor dynamics, including the natural frequencies of the rotor, to avoid resonance that could lead to mechanical failure. Additionally, the rotor must be precisely balanced to prevent excessive vibrations, which can cause wear and tear on bearings and other components.
- Sealing and Clearance Control: Minimizing steam leakage between different stages of the turbine is essential for maintaining efficiency. Engineers design precise seals and control clearances between rotating and stationary parts to reduce losses. Advanced sealing techniques, such as labyrinth seals and brush seals, are often used.
- Mechanical Integrity and Safety: The design must ensure that the turbine can operate safely under all expected conditions, including start-up, shutdown, and emergency situations. This involves designing for mechanical integrity, with components capable of withstanding high mechanical loads, thermal stresses, and the effects of transient conditions such as pressure surges or steam hammer.
- Modularity and Scalability: Modern steam turbines are often designed with modularity in mind, allowing for scalability and customization to meet different power outputs or industrial requirements. This modular approach also facilitates maintenance and component replacement.
Materials Used
The materials used in the construction of steam turbines are chosen for their ability to withstand the extreme conditions present during operation, such as high temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses. The selection of materials is crucial for ensuring the turbine’s performance, longevity, and safety.
- High-Strength Alloys: High-strength alloys, such as chromium-molybdenum steel, are commonly used for turbine rotors, casings, and other critical components. These alloys offer a good balance of strength, toughness, and resistance to thermal fatigue.
- Nickel-Based Superalloys: Nickel-based superalloys are frequently used in high-temperature sections of the turbine, such as the blades and vanes in the high-pressure stages. These superalloys are specifically designed to maintain their mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for use in environments where temperatures can exceed 1000°C.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel is used for components that require excellent corrosion resistance, such as parts exposed to wet steam or aggressive industrial environments. Austenitic stainless steels, in particular, are favored for their high-temperature performance and resistance to oxidation.
- Ceramic Coatings: To further enhance the high-temperature performance of turbine blades, ceramic coatings are often applied. These coatings provide a thermal barrier, reducing the amount of heat transferred to the underlying metal, which helps to protect against thermal degradation and extends the life of the blades.
- Titanium Alloys: Titanium alloys are sometimes used in low-pressure turbine blades due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. Their lower density compared to steel or nickel-based alloys makes them advantageous in applications where weight savings are critical.
- Creep-Resistant Materials: Creep, the tendency of materials to deform permanently under constant stress at high temperatures, is a significant concern in steam turbines. Creep-resistant materials, such as advanced ferritic steels, are used
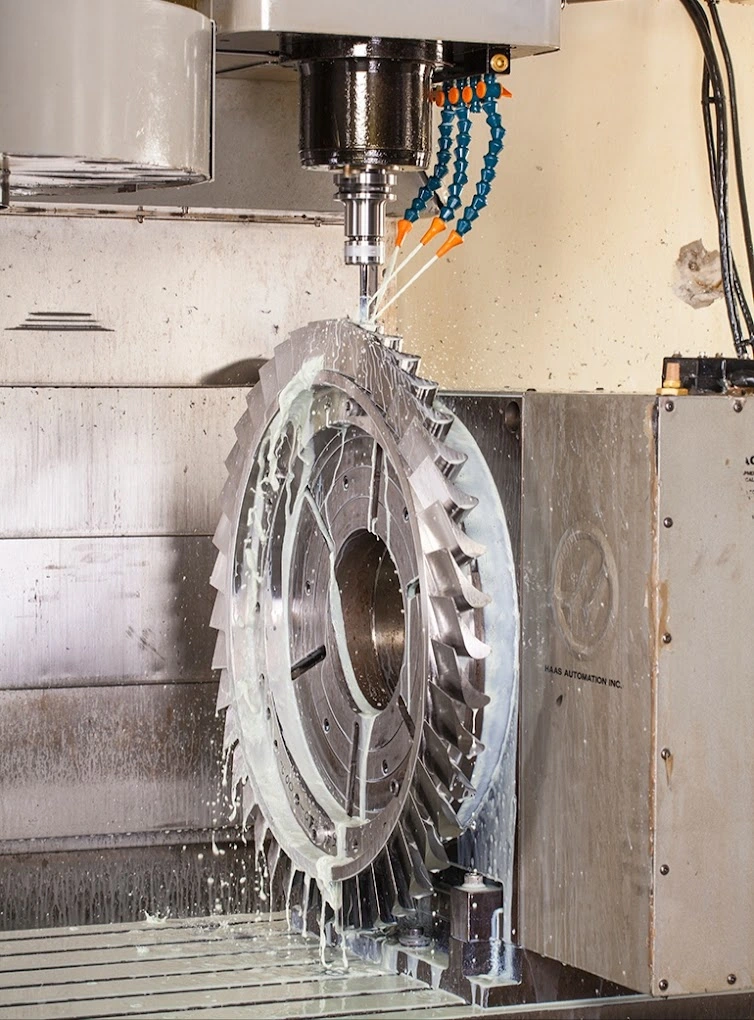
Manufacturing Techniques

The manufacturing of steam turbines involves a series of highly specialized processes that ensure the precise fabrication and assembly of components capable of withstanding extreme operational conditions. The techniques used vary depending on the size, complexity, and specific requirements of the turbine.
- Casting: Many components of steam turbines, particularly the rotor and casing, are produced using casting techniques. Casting involves pouring molten metal into a mold shaped like the final part. Once the metal solidifies, the mold is removed, leaving behind a rough component that is further refined. Investment casting and sand casting are common methods used for creating intricate parts like blades, where precision and material integrity are crucial.
- Forging: Forging is another critical manufacturing process used to create strong, high-integrity components such as rotors and discs. In forging, a metal workpiece is heated and then shaped under high pressure, which aligns the metal’s grain structure, resulting in enhanced mechanical properties. Forged components are typically stronger and more resistant to fatigue and creep than cast parts, making them ideal for high-stress areas of the turbine.
- Machining: After casting or forging, most turbine components undergo machining to achieve the necessary dimensions, surface finishes, and tolerances. Machining processes include milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. Computer numerical control (CNC) machines are often used to ensure high precision and repeatability, especially for components like blades, where aerodynamic properties are critical.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes, such as annealing, quenching, and tempering, are used to enhance the mechanical properties of turbine components. These processes alter the microstructure of the metal, improving its strength, toughness, and resistance to wear and thermal fatigue. For instance, heat treatment is crucial for blades that must maintain their integrity at high operating temperatures.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings: To protect against corrosion, erosion, and high-temperature oxidation, turbine components often undergo surface treatments and coatings. Techniques such as thermal spraying, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), and physical vapor deposition (PVD) are used to apply protective coatings. Ceramic coatings, as mentioned earlier, are commonly applied to blades to provide thermal insulation and reduce heat transfer.
- Welding and Joining: Welding is a critical process in the assembly of steam turbines, particularly for joining large sections of the casing or connecting blades to the rotor. Advanced welding techniques, such as electron beam welding and laser welding, are used to create high-strength joints with minimal defects. These techniques are especially important for maintaining the structural integrity of the turbine under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
- Balancing and Assembly: Once all the components are manufactured, they are carefully assembled. The rotor, which is one of the most critical components, must be precisely balanced to ensure smooth operation at high speeds. Balancing involves adjusting the distribution of mass around the rotor’s axis to minimize vibrations. This is typically done using specialized balancing machines that measure and correct any imbalance.
- Quality Control and Testing: Quality control is paramount in steam turbine manufacturing. Each component undergoes rigorous inspection and testing to ensure it meets the required specifications. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and dye penetrant inspection, are used to detect any internal or surface defects. The assembled turbine is also subjected to performance testing, where it is run under controlled conditions to verify its efficiency, output, and operational stability.
- Final Assembly and Installation: After passing all tests, the turbine is finally assembled and prepared for shipment to its installation site. Installation requires precise alignment and calibration to ensure that the turbine operates correctly within its intended system, whether it’s a power plant, industrial facility, or marine vessel. The installation process includes integrating the turbine with the steam supply, electrical systems, and other necessary infrastructure.
Operation and Maintenance
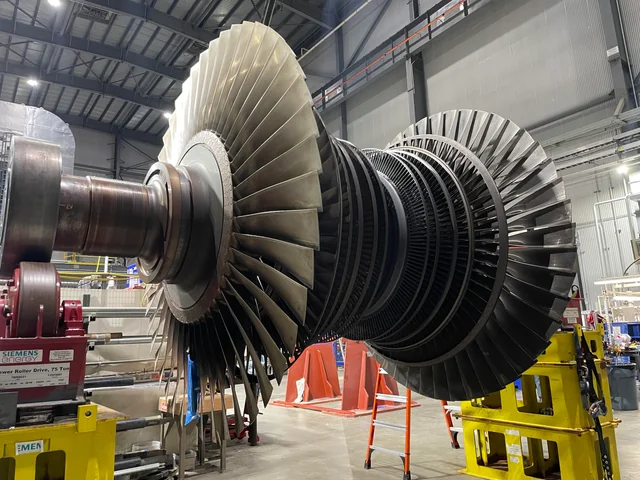

Operating Conditions
Steam turbines operate under demanding conditions, where factors such as temperature, pressure, steam quality, and load variations can significantly impact their performance and longevity. Understanding these conditions is essential for optimizing turbine operation and ensuring reliable performance.
- Temperature and Pressure: Steam turbines are designed to operate at high temperatures and pressures. In typical power generation applications, steam enters the turbine at temperatures ranging from 500°C to 600°C and pressures up to 30 MPa (megapascals). These extreme conditions enable the turbine to extract maximum energy from the steam, but they also impose significant thermal and mechanical stresses on the components.
- Steam Quality: The quality of the steam entering the turbine is critical for efficient operation. Ideally, the steam should be dry and superheated to prevent condensation inside the turbine, which can lead to erosion of the blades and reduced efficiency. However, in some applications, such as nuclear power plants, saturated steam may be used, requiring careful design and operation to manage the associated risks.
- Load Variations: Steam turbines often operate under varying loads, depending on the demand for electricity or the specific requirements of the industrial process they are powering. The ability to quickly and efficiently respond to load changes is crucial for maintaining stable operation. Turbines must be capable of ramping up or down without excessive wear or risk of damage.
- Startup and Shutdown Procedures: The processes of starting up and shutting down a steam turbine are critical periods that require careful control. During startup, the turbine components must be gradually brought up to operating temperature to avoid thermal shocks, which can cause cracking or deformation. Similarly, shutdown procedures involve slowly cooling the turbine to prevent damage.
- Control Systems: Modern steam turbines are equipped with sophisticated control systems that manage various operational parameters, such as steam flow, temperature, pressure, and rotational speed. These systems ensure that the turbine operates within its design limits and responds appropriately to changes in load or other operating conditions.
Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the long-term reliability and efficiency of steam turbines. Maintenance practices are typically divided into preventive, predictive, and corrective maintenance.
- Preventive Maintenance: Preventive maintenance involves routine inspections and servicing of the turbine to prevent potential issues from arising. This includes tasks such as:
- Lubrication: Regular lubrication of bearings and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
- Inspection of Blades and Seals: Checking for signs of wear, erosion, or corrosion on turbine blades and seals.
- Cleaning: Removing deposits or scale from turbine components to maintain optimal performance.
- Calibration: Ensuring that control systems and sensors are accurately calibrated to prevent operational errors.
- Predictive Maintenance: Predictive maintenance uses condition monitoring techniques to predict when maintenance is needed before a failure occurs. This approach allows for maintenance to be scheduled based on the actual condition of the turbine rather than on a fixed schedule. Key techniques include:
- Vibration Analysis: Monitoring the vibrations of the turbine to detect imbalances, misalignment, or bearing issues.
- Thermography: Using infrared cameras to detect hotspots or uneven temperature distributions that may indicate a problem.
- Oil Analysis: Analyzing the lubrication oil for signs of contamination, wear particles, or chemical degradation.
- Corrective Maintenance: When a component fails or a problem is detected, corrective maintenance is performed to repair or replace the affected parts. This type of maintenance can involve:
- Blade Replacement: Replacing damaged or worn blades to restore turbine efficiency and prevent further damage.
- Seal Repair or Replacement: Addressing issues with seals that may cause steam leakage or reduced efficiency.
- Bearing Replacement: Replacing worn or damaged bearings to prevent rotor imbalance and excessive vibrations.
- Outage Planning: Steam turbines typically undergo scheduled outages for extensive inspections, repairs, and overhauls. These outages are carefully planned to minimize downtime and ensure that the turbine is returned to service in optimal condition. During an outage, the turbine may be disassembled, with major components like the rotor, blades, and casing inspected and refurbished as necessary.
Common Issues and Solutions
Steam turbines, despite their robust design, can encounter various issues during operation. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly is key to maintaining reliable performance.
- Blade Fouling and Erosion: Fouling occurs when deposits form on the turbine blades, often as a result of impurities in the steam. Erosion, on the other hand, is caused by high-velocity steam or water droplets impinging on the blades, gradually wearing away the material. These issues can lead to reduced efficiency and, if left unchecked, can cause serious damage.
- Solution: Regular cleaning and maintenance can prevent fouling, while erosion-resistant coatings can extend blade life. Additionally, improving the quality of the steam entering the turbine can reduce the risk of these problems.
- Vibration and Rotor Imbalance: Excessive vibration is a common issue in steam turbines and can be caused by rotor imbalance, misalignment, bearing wear, or other mechanical problems. Vibration can lead to accelerated wear of components and, in severe cases, catastrophic failure.
- Solution: Vibration analysis and regular balancing of the rotor can help detect and correct these issues before they cause significant damage. Proper alignment during installation and routine bearing inspections are also critical.
- Steam Leakage: Steam leakage can occur due to worn seals, poor sealing surfaces, or cracks in the casing. This leads to a loss of efficiency and can also cause damage to surrounding components.
- Solution: Regular inspection of seals and replacement when necessary can mitigate steam leakage. In some cases, upgrading to more advanced sealing technologies, such as brush seals, can provide a better seal and longer service life.
- Thermal Fatigue and Creep: Thermal fatigue occurs when turbine components are subjected to repeated cycles of heating and cooling, leading to the formation of cracks. Creep is a gradual deformation of materials under constant high temperature and stress. Both issues can significantly impact the structural integrity of the turbine.
- Solution: Using materials specifically designed to resist thermal fatigue and creep, along with careful control of operating conditions, can minimize these risks. Regular inspection and monitoring for signs of fatigue or creep are also essential.
- Control System Failures: The control systems of steam turbines are vital for safe and efficient operation. Failures in these systems can lead to incorrect steam flow, pressure surges, or even turbine trips.
- Solution: Regular testing and calibration of control systems, along with the use of redundant systems, can help prevent control system failures. Upgrading older systems to modern, digital control systems can also enhance reliability.
Applications of Steam Turbines
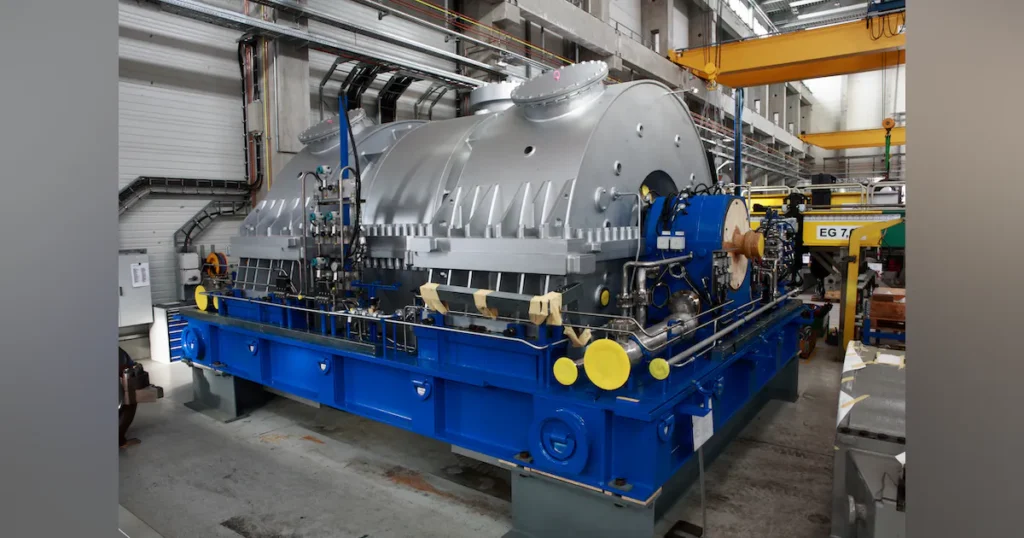

Power Generation
Steam turbines are central to power generation and are used in a variety of settings, from large-scale thermal power plants to smaller, decentralized energy systems. The following subsections outline the main applications of steam turbines in power generation:
- Coal-Fired Power Plants:
- Overview: Coal-fired power plants have historically been one of the most common applications of steam turbines. In these plants, coal is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam, which is then directed into a steam turbine to generate electricity.
- Role of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines in coal-fired plants are designed to handle the high temperatures and pressures associated with coal combustion. They convert the thermal energy from the steam into mechanical energy, which drives an electrical generator.
- Environmental Considerations: While coal-fired power plants are efficient, they are also a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. Many modern plants incorporate emission control technologies and are transitioning to cleaner coal technologies, such as supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam cycles, to improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Nuclear Power Plants:
- Overview: In nuclear power plants, steam turbines are used to convert the thermal energy generated by nuclear fission into electricity. These plants use nuclear reactors to heat water and produce steam.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The steam produced in a nuclear reactor is typically at a lower temperature and pressure compared to that in fossil-fuel plants. However, the turbines must be extremely reliable and durable due to the safety-critical nature of nuclear power generation. The turbines in nuclear plants are often large, with high power outputs to match the continuous energy production of the reactor.
- Special Considerations: The design of steam turbines for nuclear power includes considerations for safety, such as the ability to operate reliably under potential emergency conditions and withstand the corrosive effects of certain types of steam.
- Gas-Fired Power Plants (Combined Cycle):
- Overview: Combined cycle power plants use both gas and steam turbines to generate electricity. In these plants, a gas turbine generates electricity and its exhaust heat is used to produce steam, which then powers a steam turbine.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The steam turbine in a combined cycle plant enhances the overall efficiency of the plant by utilizing the waste heat from the gas turbine. This process significantly increases the plant’s thermal efficiency, often reaching levels above 60%.
- Advantages: Combined cycle plants are known for their high efficiency, flexibility, and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional coal-fired plants. Steam turbines in these plants are integral to achieving these benefits.
- Geothermal Power Plants:
- Overview: Geothermal power plants use steam turbines to generate electricity from geothermal energy, which is the heat stored within the Earth.
- Role of Steam Turbines: In geothermal plants, steam is extracted from underground reservoirs and used to drive turbines. These turbines must be designed to handle steam with varying temperatures and pressures, as well as the potential presence of corrosive gases and minerals.
- Challenges and Solutions: The main challenges in geothermal power generation include scaling, corrosion, and the management of non-condensable gases. Turbine designs that include corrosion-resistant materials and advanced sealing technologies are essential for long-term operation in these environments.
- Solar Thermal Power Plants:
- Overview: Solar thermal power plants, also known as concentrating solar power (CSP) plants, use steam turbines to generate electricity from solar energy.
- Role of Steam Turbines: In CSP plants, mirrors or lenses concentrate sunlight to heat a fluid, which is then used to produce steam. The steam drives a turbine, converting thermal energy into mechanical energy for electricity generation.
- Innovations: Some CSP plants incorporate thermal storage systems, allowing them to generate electricity even when the sun is not shining. The steam turbines in these plants must be adaptable to varying steam inputs and capable of operating efficiently with the thermal storage systems.
Industrial Applications
Beyond power generation, steam turbines are widely used in various industrial processes where they provide mechanical power for a range of applications.
- Petrochemical Industry:
- Overview: Steam turbines are essential in the petrochemical industry, where they are used to drive compressors, pumps, and other machinery involved in the processing of chemicals and petroleum products.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The turbines in this industry are often designed for continuous operation, high efficiency, and reliability under harsh conditions, including high temperatures and corrosive environments.
- Advantages: Using steam turbines in petrochemical plants helps improve overall energy efficiency by recovering waste heat and converting it into useful mechanical or electrical energy.
- Pulp and Paper Industry:
- Overview: The pulp and paper industry relies on steam turbines for both electricity generation and mechanical drives in processes such as pulping, drying, and paper making.
- Role of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines in this industry often operate in cogeneration setups, where they simultaneously produce electricity and steam for the manufacturing process. This combined heat and power (CHP) approach enhances energy efficiency.
- Challenges: The main challenges include handling fluctuating loads and ensuring reliable operation in environments with high moisture content and potential corrosive chemicals.
- Steel Manufacturing:
- Overview: In steel manufacturing, steam turbines are used to drive blowers, compressors, and rolling mills. The steam used often comes from waste heat recovery systems, making the process more energy-efficient.
- Role of Steam Turbines: Steam turbines help reduce the overall energy consumption of steel mills by utilizing waste heat to generate power for various processes.
- Benefits: Integrating steam turbines into steel manufacturing processes not only reduces energy costs but also helps in meeting environmental regulations by lowering emissions.
- Sugar Industry:
- Overview: The sugar industry uses steam turbines extensively in the production of sugar and ethanol. The turbines are part of the cogeneration systems that use bagasse (the fibrous residue left after extracting sugar juice) as fuel.
- Role of Steam Turbines: In this industry, steam turbines generate electricity and provide mechanical power for the crushing and refining processes. The use of biomass like bagasse makes the process more sustainable and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
- Sustainability: The integration of steam turbines into sugar production highlights the potential for renewable energy sources in industrial applications.
Marine Propulsion
Steam turbines have a long history of use in marine propulsion, particularly in naval vessels and large commercial ships. Their reliability, efficiency, and power output make them ideal for this demanding application.
- Naval Vessels:
- Overview: Steam turbines have been a mainstay in naval propulsion, especially in large vessels such as aircraft carriers, destroyers, and submarines.
- Role of Steam Turbines: Naval turbines are designed for high power output, reliability, and efficiency. They must operate under extreme conditions, including rapid speed changes and prolonged high-speed operation.
- Advancements: Modern naval steam turbines often incorporate advanced materials and cooling technologies to withstand the harsh marine environment and to operate quietly, which is crucial for stealth in military operations.
- Commercial Shipping:
- Overview: In commercial shipping, steam turbines are used in large vessels such as tankers and bulk carriers. Although diesel engines have become more common, steam turbines are still used in certain applications, particularly where high power and long-range operation are required.
- Advantages: Steam turbines offer smooth operation, reduced vibration, and lower maintenance requirements compared to other propulsion systems, making them suitable for large ships.
- Trends: The use of steam turbines in commercial shipping has declined with the rise of more fuel-efficient diesel engines. However, they remain in use in specific scenarios where their benefits outweigh those of alternative technologies.
Renewable Energy Integration
Steam turbines are also finding applications in renewable energy systems, contributing to the generation of clean and sustainable energy.
- Biomass Power Plants:
- Overview: Biomass power plants use organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and waste, to produce steam, which then drives turbines to generate electricity.
- Role of Steam Turbines: In biomass plants, steam turbines must handle steam generated from a variety of biomass sources, which can vary in quality and consistency. The turbines are designed to be flexible and efficient, maximizing the energy extracted from biomass.
- Environmental Benefits: Biomass power generation is considered carbon-neutral, as the CO2 released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during the growth of the biomass. Steam turbines play a key role in making this a viable and sustainable energy source.
- Concentrated Solar Power (CSP):
- Overview: In CSP plants, steam turbines are used to convert solar energy into electricity. The plants use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, where it heats a fluid to produce steam.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The turbines in CSP plants must be designed to operate efficiently with steam generated from fluctuating solar input, as well as to integrate with thermal storage systems that allow for power generation even when the sun is not shining.
- Innovation and Future Potential: As CSP technology advances, steam turbines are expected to play an increasingly important role in providing renewable, dispatchable power, helping to stabilize grids with high penetration of intermittent renewable sources like wind and solar PV.
Efficiency and Performance Optimization
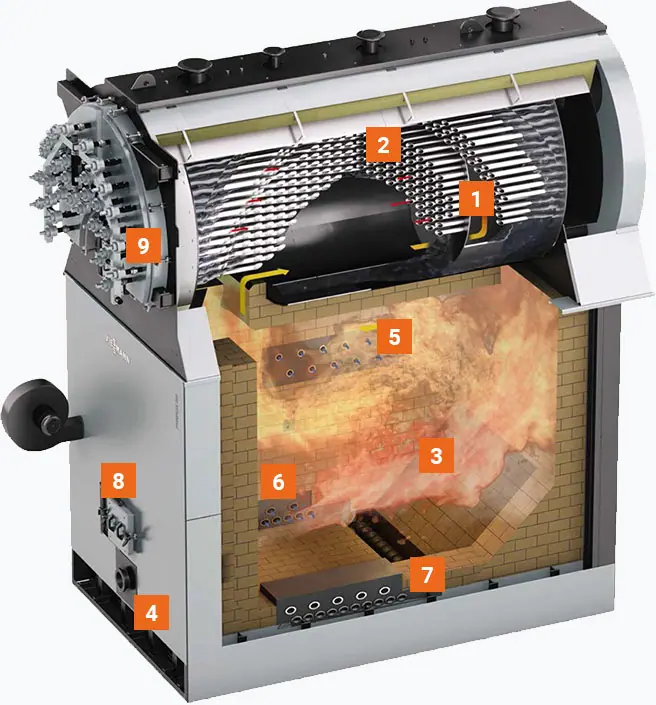

Factors Affecting Efficiency
The efficiency of a steam turbine is a critical aspect of its performance, influencing the overall energy conversion process and the economic viability of power plants and industrial applications. Several factors can impact the efficiency of a steam turbine:
- Steam Conditions:
- Temperature and Pressure: The higher the steam temperature and pressure at the turbine inlet, the greater the potential for energy extraction. Superheated steam, with higher energy content, allows the turbine to produce more work, thereby increasing efficiency. However, materials and design must be capable of withstanding these extreme conditions.
- Steam Quality: The quality of steam, particularly its dryness fraction, affects turbine performance. Wet steam can cause erosion of turbine blades and reduce efficiency due to the presence of water droplets. Maintaining a high dryness fraction or superheating the steam minimizes these losses.
- Design and Aerodynamics:
- Blade Design: The design of turbine blades, including their shape, angle, and surface finish, plays a significant role in efficiency. Aerodynamically optimized blades reduce losses due to friction and turbulence, allowing for more effective energy conversion from steam to mechanical work.
- Stage Efficiency: Steam turbines are often divided into multiple stages, each designed to extract energy from steam at progressively lower pressures. The efficiency of each stage contributes to the overall turbine efficiency. Proper staging, with carefully calculated blade profiles and angles, is essential for maximizing efficiency.
- Mechanical Losses:
- Friction and Wear: Mechanical losses due to friction in bearings, seals, and other moving parts can reduce overall turbine efficiency. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and the use of advanced materials can help minimize these losses.
- Vibration and Imbalance: Imbalances in the rotor or excessive vibrations can lead to mechanical inefficiencies, as energy is lost in the form of unwanted movements. Ensuring that the turbine is properly balanced and that vibrations are controlled through effective damping mechanisms is crucial.
- Thermodynamic Losses:
- Heat Losses: Heat losses occur when steam or other components transfer heat to the surrounding environment. Proper insulation of the turbine casing and piping, as well as minimizing the temperature gradient within the turbine, can help reduce these losses.
- Entropy Generation: Inefficiencies in the expansion process within the turbine stages can lead to increased entropy, reducing the available work output. Reducing these losses involves optimizing the expansion process and minimizing irreversible losses within the turbine.
Optimization Techniques
Improving the efficiency of steam turbines involves a combination of design optimization, operational strategies, and technological innovations. The following techniques are commonly used to enhance turbine performance:
- Advanced Blade Design:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CFD is widely used in the design and optimization of turbine blades. By simulating the flow of steam through the turbine, engineers can identify areas where losses occur and adjust blade shapes and angles to improve efficiency. CFD allows for the testing of multiple design iterations in a virtual environment, reducing the need for physical prototypes.
- 3D Blade Profiling: Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing and precision machining, enable the production of complex blade profiles that are tailored to specific operating conditions. 3D blade profiling can result in blades that offer better aerodynamic performance and reduced losses.
- Steam Temperature and Pressure Control:
- Superheating and Reheating: Increasing the temperature of steam before it enters the turbine (superheating) or reheating steam between turbine stages can significantly improve efficiency. Reheating, in particular, allows for more energy extraction by reducing the moisture content in the later stages of the turbine.
- Pressure Optimization: Operating the turbine at the optimal steam pressure for each stage can maximize efficiency. This involves careful control of steam pressure throughout the turbine, ensuring that each stage operates at its most efficient point on the pressure-enthalpy curve.
- Energy Recovery Systems:
- Regenerative Feedwater Heating: Regenerative feedwater heating is a technique where steam is extracted from intermediate stages of the turbine and used to preheat the feedwater before it enters the boiler. This reduces the amount of fuel needed to reach the desired steam temperature, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the Rankine cycle.
- Condensate Recovery: Efficient recovery and reuse of condensate (water) from the turbine exhaust can reduce the energy required to heat and pressurize water for subsequent cycles. This also minimizes the need for additional water treatment, contributing to overall efficiency improvements.
- Load Optimization:
- Variable Load Operation: Modern steam turbines are designed to operate efficiently across a range of loads, not just at full capacity. By optimizing turbine performance under partial loads, power plants can improve overall efficiency, especially in applications where demand fluctuates throughout the day.
- Load Matching: Load matching involves adjusting the turbine’s operation to match the specific energy demand at any given time. This can involve varying the steam flow rate, adjusting the number of active turbine stages, or modulating the turbine’s output to match real-time load requirements.
- Monitoring and Control Systems:
- Real-Time Performance Monitoring: Advanced sensors and control systems allow for real-time monitoring of turbine performance, including temperature, pressure, vibration, and efficiency metrics. By continuously monitoring these parameters, operators can make adjustments to optimize performance and prevent issues before they lead to inefficiencies or failures.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using data analytics and machine learning, predictive maintenance systems can forecast potential issues based on historical performance data. This allows for maintenance to be performed proactively, reducing downtime and improving overall turbine efficiency.
Monitoring and Performance Analysis
Maintaining optimal efficiency in steam turbines requires ongoing monitoring and analysis of performance data. The following approaches are commonly used to assess and enhance turbine efficiency:
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Heat Rate: The heat rate is a measure of the amount of energy used by the turbine to generate electricity. It is typically expressed as the amount of fuel energy required per unit of electrical output (e.g., BTU/kWh). Monitoring the heat rate helps identify inefficiencies in fuel use and overall turbine performance.
- Thermal Efficiency: Thermal efficiency measures the ratio of useful work output to the total heat input. It is a key indicator of how effectively the turbine converts thermal energy into mechanical energy. Higher thermal efficiency indicates better performance.
- Capacity Factor: The capacity factor is the ratio of the actual output of the turbine over a period of time to its maximum possible output. It reflects how well the turbine is being utilized relative to its full capacity.
- Performance Testing:
- Acceptance Testing: Acceptance testing is conducted when a turbine is first installed or after a major overhaul to ensure it meets the specified performance criteria. These tests typically measure parameters such as output power, efficiency, and steam consumption under controlled conditions.
- Routine Testing: Periodic performance testing is conducted to monitor the ongoing efficiency of the turbine. Routine tests help detect gradual declines in performance, allowing for timely interventions to restore efficiency.
- Data Analytics and Optimization:
- Data Logging and Trend Analysis: Continuous data logging allows for the collection of vast amounts of performance data, which can be analyzed to identify trends, detect anomalies, and assess the impact of operational changes on efficiency.
- Digital Twins: A digital twin is a virtual model of the steam turbine that simulates its real-world counterpart in real time. By comparing the digital twin’s performance with actual operational data, operators can identify inefficiencies and test potential optimizations without risking the physical turbine.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Vibration Monitoring: Vibration analysis is a critical diagnostic tool for detecting mechanical issues such as rotor imbalance, misalignment, or bearing wear. By identifying and correcting these issues early, operators can prevent efficiency losses and extend the life of the turbine.
- Thermal Imaging: Thermal imaging is used to detect hotspots and assess the distribution of temperature across the turbine components. This helps identify areas where heat losses are occurring and where insulation or cooling might be needed.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
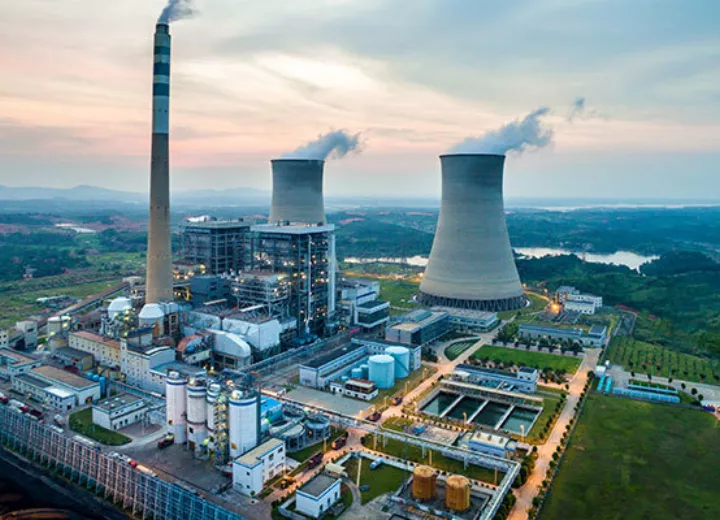

Environmental Concerns
Steam turbines, while crucial to power generation and industrial processes, are associated with several environmental concerns. These issues stem primarily from the energy sources used to produce steam and the byproducts of turbine operation.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
- Fossil Fuel Combustion: Steam turbines used in coal, oil, and natural gas-fired power plants contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2). The combustion of fossil fuels releases CO2, which is a major contributor to global warming and climate change.
- Mitigation Strategies: Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions include improving the efficiency of steam turbines, transitioning to cleaner fuels, and integrating carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. Higher efficiency means that less fuel is required to produce the same amount of electricity, thereby reducing emissions per unit of energy generated.
- Air Pollutants:
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Fossil fuel combustion in power plants can release harmful air pollutants, including SO2 and NOx, which contribute to acid rain and respiratory problems in humans. These pollutants are particularly prevalent in coal-fired power plants, where sulfur content in the fuel is higher.
- Control Technologies: Technologies such as flue gas desulfurization (FGD) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) are used to reduce SO2 and NOx emissions from power plants. Additionally, low-NOx burners and other combustion optimization techniques help minimize the formation of these pollutants at the source.
- Water Usage and Thermal Pollution:
- Cooling Water Requirements: Steam turbines, particularly in large power plants, require substantial amounts of water for cooling. The withdrawal of water from natural sources can impact local ecosystems, especially if not managed sustainably. Furthermore, the discharge of heated water back into the environment can cause thermal pollution, which negatively affects aquatic life.
- Mitigation Strategies: To mitigate these impacts, power plants can adopt closed-loop cooling systems that minimize water withdrawal and reduce thermal discharge. Additionally, dry cooling systems, which use air instead of water, are increasingly being implemented, particularly in water-scarce regions.
- Solid Waste and Byproducts:
- Coal Ash and Slag: The combustion of coal in power plants produces solid byproducts such as ash and slag, which can contain heavy metals and other toxic substances. These byproducts must be managed carefully to prevent soil and water contamination.
- Disposal and Reuse: Modern waste management practices include the safe disposal of ash in lined landfills and the beneficial reuse of ash in construction materials, such as cement and concrete. By converting waste into valuable products, the environmental impact of coal ash can be minimized.
Sustainability Initiatives
In response to environmental concerns, the steam turbine industry is increasingly adopting sustainability initiatives aimed at reducing its environmental footprint and supporting the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Integration with Renewable Energy:
- Biomass and Waste-to-Energy: Steam turbines are being integrated with renewable energy sources such as biomass and waste-to-energy plants. These systems use organic waste materials to produce steam, which is then converted into electricity by steam turbines. Biomass is considered carbon-neutral, as the CO2 released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during the growth of the biomass.
- Geothermal and Solar Thermal: Geothermal and concentrated solar power (CSP) plants also utilize steam turbines to generate electricity. These renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making them attractive options for sustainable power generation. The use of steam turbines in these settings supports the broader adoption of renewable energy technologies.
- Efficiency Improvements:
- Supercritical and Ultra-Supercritical Steam Cycles: Advancements in turbine technology have led to the development of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam cycles, which operate at higher temperatures and pressures than conventional steam cycles. These cycles achieve higher efficiencies, meaning that less fuel is needed to produce the same amount of electricity, resulting in lower emissions.
- Cogeneration and Combined Heat and Power (CHP): Cogeneration, or CHP, systems simultaneously produce electricity and useful heat from the same energy source. By capturing and utilizing the waste heat from steam turbines, CHP systems significantly improve overall energy efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):
- CCS Technology: Carbon capture and storage is a technology designed to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and industrial processes, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. The captured CO2 is then transported and stored underground in geological formations. When integrated with steam turbines, CCS can greatly reduce the carbon footprint of fossil fuel-based power generation.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While CCS has the potential to mitigate climate change, it faces challenges such as high costs, energy requirements, and the need for suitable storage sites. However, ongoing research and development efforts aim to overcome these barriers, making CCS a viable option for large-scale emission reductions.
- Material and Resource Efficiency:
- Recycling and Waste Minimization: The steam turbine industry is adopting practices to minimize waste and improve resource efficiency. This includes the recycling of metals and other materials used in turbine manufacturing, as well as the reduction of material waste through precision manufacturing techniques.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Life cycle assessment is a tool used to evaluate the environmental impacts of a product throughout its entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. By conducting LCAs, manufacturers can identify areas where environmental impacts can be reduced, leading to more sustainable turbine production and operation.
Regulatory Framework
The operation of steam turbines, particularly in power generation, is subject to a range of environmental regulations aimed at minimizing their impact on the environment. These regulations vary by region but generally focus on emissions control, water usage, and waste management.
- Emissions Regulations:
- Clean Air Act (U.S.): In the United States, the Clean Air Act (CAA) regulates air emissions from power plants and industrial sources, including those using steam turbines. The CAA establishes limits for pollutants such as SO2, NOx, and particulate matter, and mandates the use of best available control technologies (BACT) to reduce emissions.
- European Union Emissions Trading System (EU ETS): The EU ETS is a cap-and-trade system that sets a limit on the total amount of greenhouse gases that can be emitted by certain industries, including power generation. Steam turbine operators in the EU must comply with emission allowances or purchase additional allowances if they exceed their limits.
- Water Usage and Discharge Regulations:
- Clean Water Act (U.S.): The Clean Water Act (CWA) regulates the discharge of pollutants into U.S. waters and sets standards for water quality. Power plants using steam turbines must obtain permits for water withdrawal and discharge, ensuring that their operations do not harm aquatic ecosystems.
- EU Water Framework Directive: In the European Union, the Water Framework Directive establishes a framework for protecting water resources, including the regulation of water usage and thermal discharges from power plants. Compliance with these regulations is essential for the sustainable operation of steam turbines.
- Waste Management and Disposal:
- Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA): In the U.S., the RCRA governs the management of hazardous and non-hazardous waste, including coal ash from power plants. The act requires safe disposal practices and encourages the recycling and reuse of industrial byproducts.
- EU Waste Framework Directive: The EU Waste Framework Directive sets guidelines for waste management across member states, promoting recycling and the reduction of waste generation. Steam turbine operators must comply with these regulations to minimize their environmental impact.
- International Standards and Guidelines:
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management Systems: The ISO 14001 standard provides a framework for organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities in a systematic manner. Compliance with ISO 14001 helps steam turbine operators reduce their environmental footprint and improve sustainability.
- World Bank Environmental and Social Standards: The World Bank’s Environmental and Social Standards (ESS) provide guidelines for managing environmental and social risks in projects financed by the World Bank. These standards are often used in the development of power plants and other large-scale projects involving steam turbines.
Future Trends and Innovations
Technological Advances
The steam turbine industry is continuously evolving, driven by the need for greater efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance. Several technological advances are shaping the future of steam turbines:
- Advanced Materials:
- Superalloys: The development of advanced nickel-based superalloys is enabling steam turbines to operate at higher temperatures and pressures, which improves efficiency. These materials are designed to resist creep, corrosion, and thermal fatigue, making them ideal for use in the most demanding sections of the turbine.
- Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs): CMCs are gaining attention for their potential to replace traditional metal alloys in high-temperature turbine components. These materials offer excellent thermal stability, low density, and resistance to oxidation, allowing turbines to operate at even higher temperatures without compromising structural integrity.
- Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing is revolutionizing the production of turbine components. This technology allows for the creation of complex, optimized geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. Additive manufacturing also reduces material waste and shortens production times.
- Advanced Blade Design:
- 3D-Aerodynamic Blades: Innovations in blade design, particularly through the use of 3D aerodynamic modeling, are improving the efficiency and performance of steam turbines. These blades are designed to optimize the flow of steam, reducing losses due to turbulence and friction. The use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations allows engineers to refine blade shapes for maximum efficiency.
- Shrouded and Shroudless Blades: Shrouded blades, which include a cover on the blade tips to reduce leakage, are being optimized to further improve efficiency. At the same time, advancements in shroudless blade designs are being explored to reduce weight and mechanical complexity while maintaining aerodynamic performance.
- Digitalization and Smart Turbines:
- Digital Twins: The concept of a digital twin, a virtual model of the steam turbine that runs in parallel with the physical machine, is becoming a critical tool in the industry. Digital twins allow operators to monitor turbine performance in real-time, predict maintenance needs, and optimize operations. By simulating different scenarios, digital twins can help identify potential issues before they occur and suggest the best course of action for maintenance or operational adjustments.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being increasingly used to enhance turbine control systems. These technologies enable more precise control of operating parameters, such as steam flow, pressure, and temperature, optimizing turbine efficiency under varying load conditions. AI-driven analytics can also predict equipment failures, reducing downtime and extending the life of turbine components.
- Modular and Scalable Designs:
- Modularity: The development of modular steam turbines is a trend aimed at improving flexibility and reducing costs. Modular turbines can be easily scaled up or down depending on the power generation requirements, making them suitable for both large-scale power plants and smaller, decentralized energy systems. Modularity also facilitates easier maintenance and component replacement, reducing downtime.
- Scalability for Microgrids: Steam turbines are being adapted for use in microgrids and distributed energy systems. These scalable turbines are designed to provide reliable power in remote locations or as part of a hybrid energy system that integrates renewable energy sources with traditional power generation.
Integration with Smart Grids
As the energy landscape evolves, steam turbines are being integrated into smart grid systems, which offer enhanced flexibility, reliability, and efficiency in power generation and distribution.
- Role of Steam Turbines in Smart Grids:
- Load Balancing: Steam turbines are essential in smart grids for load balancing, especially during peak demand periods. They can be ramped up or down to match the demand, helping to maintain grid stability and prevent blackouts. The ability to quickly respond to changes in demand makes steam turbines a valuable component of smart grids.
- Integration with Renewable Energy: Smart grids are increasingly incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. Steam turbines, particularly those in combined heat and power (CHP) plants, can provide backup power when renewable sources are intermittent, ensuring a continuous and reliable energy supply. By integrating with smart grid technologies, steam turbines can optimize their operation based on real-time data from the grid.
- Advanced Control Systems:
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control: Advanced control systems are being developed to allow steam turbines to operate more efficiently within a smart grid. These systems use real-time data to adjust operating parameters, such as steam pressure and temperature, to optimize performance. Real-time monitoring also helps detect potential issues before they lead to failures, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Grid Synchronization: Steam turbines are being equipped with advanced synchronization technologies that allow them to seamlessly integrate with smart grids. These technologies ensure that the turbines can synchronize their output with the grid’s frequency and voltage, maintaining power quality and reliability.
- Demand Response and Energy Storage:
- Demand Response Programs: Steam turbines are playing a role in demand response programs, where power generation is adjusted based on real-time demand. In these programs, steam turbines can reduce their output during periods of low demand or increase it during peak times, helping to balance the grid and reduce the need for additional peaking power plants.
- Integration with Energy Storage: Steam turbines are being integrated with energy storage systems, such as batteries and thermal storage, to enhance their flexibility and efficiency. Energy storage allows turbines to store excess energy produced during periods of low demand and release it when needed, improving overall grid stability and efficiency.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development (R&D) efforts are focused on advancing steam turbine technology to meet the evolving demands of the energy industry and address environmental challenges.
- High-Efficiency Steam Cycles:
- Supercritical and Ultra-Supercritical Cycles: R&D is driving the development of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam cycles, which operate at higher temperatures and pressures than conventional cycles. These advanced cycles offer higher thermal efficiencies, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that can withstand the extreme conditions of these cycles.
- Thermodynamic Cycle Innovations: Innovative thermodynamic cycles, such as the Kalina cycle and the Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC), are being explored for their potential to improve efficiency in specific applications. These cycles use different working fluids or configurations to optimize energy conversion, particularly in low-temperature or waste heat recovery applications.
- Low-Carbon and Carbon-Neutral Technologies:
- Hydrogen-Fueled Steam Turbines: Research is underway to develop steam turbines that can operate on hydrogen, a carbon-free fuel that can be produced using renewable energy. Hydrogen-fueled turbines have the potential to provide reliable, low-carbon power generation, particularly in conjunction with renewable energy sources.
- Carbon Capture Integration: Integrating carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies with steam turbines is a key area of research aimed at reducing CO2 emissions from fossil fuel-based power generation. Ongoing R&D efforts are focused on improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of CCS, making it a viable option for large-scale deployment.
- Enhanced Durability and Reliability:
- Advanced Coatings and Surface Treatments: R&D is focused on developing advanced coatings and surface treatments that can extend the life of turbine components by protecting them from corrosion, erosion, and high-temperature oxidation. These coatings are essential for improving the durability and reliability of turbines operating under harsh conditions.
- Predictive Maintenance and AI: Research into predictive maintenance technologies, powered by AI and machine learning, is helping to improve the reliability of steam turbines. By analyzing historical performance data and identifying patterns that precede failures, these technologies enable more accurate predictions of maintenance needs, reducing unexpected downtime and extending the lifespan of turbine components.
Challenges and Opportunities
As the steam turbine industry evolves, it faces a range of challenges and opportunities that will shape its future.
- Challenges:
- Environmental Regulations: Increasingly stringent environmental regulations, particularly those related to greenhouse gas emissions and water usage, pose a challenge for the steam turbine industry. Meeting these regulations requires ongoing innovation in turbine design, materials, and operational strategies.
- Competition from Alternative Technologies: The rise of alternative power generation technologies, such as wind, solar, and energy storage, presents a challenge to the steam turbine industry. These technologies are becoming more cost-competitive and are often favored in policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
- Aging Infrastructure: Many existing steam turbines, particularly those in older power plants, are reaching the end of their operational life. Upgrading or replacing these turbines with more efficient, modern designs presents a significant challenge, particularly in terms of cost and downtime.
- Opportunities:
- Decarbonization Initiatives: The global push for decarbonization presents an opportunity for the steam turbine industry to develop low-carbon and carbon-neutral technologies. This includes the integration of steam turbines with renewable energy sources, hydrogen, and CCS technologies.
- Energy Transition: As the energy industry transitions towards more sustainable sources, steam turbines have the opportunity to play a key role in hybrid systems that combine renewable energy with traditional power generation. These hybrid systems can provide reliable, continuous power while reducing overall carbon emissions.
- Emerging Markets: Emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, present significant growth opportunities for the steam turbine industry. As these regions continue to industrialize and expand their energy infrastructure, the demand for reliable and efficient power generation technologies, including steam turbines, is expected to increase.
Case Studies and Industry Examples

Notable Projects
Real-world applications of steam turbines showcase their versatility and efficiency across various industries. The following case studies highlight significant installations and the impact of steam turbines in different settings:
- The Taichung Power Plant, Taiwan:
- Overview: The Taichung Power Plant is one of the largest coal-fired power plants in the world, located in Taiwan. With an installed capacity of 5,500 MW, it plays a critical role in meeting the energy demands of Taiwan’s population and industry.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The plant uses a series of large-scale steam turbines to convert the thermal energy from coal combustion into electricity. These turbines are designed to operate at high efficiency, utilizing supercritical steam conditions to maximize energy extraction.
- Environmental Impact: Despite being a coal-fired plant, Taichung has implemented advanced emission control technologies, including flue gas desulfurization and selective catalytic reduction, to minimize its environmental footprint. The plant also serves as a benchmark for efficiency improvements in large-scale fossil fuel power generation.
- The Olkaria Geothermal Plant, Kenya:
- Overview: The Olkaria Geothermal Plant is the largest geothermal power plant in Africa, located in Kenya’s Great Rift Valley. It has a capacity of over 800 MW and contributes significantly to Kenya’s renewable energy mix.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The plant utilizes steam turbines specifically designed to handle the unique challenges of geothermal steam, such as the presence of corrosive gases and minerals. The turbines efficiently convert geothermal energy into electricity, providing a reliable source of power with low carbon emissions.
- Sustainability: The success of the Olkaria Geothermal Plant demonstrates the potential of geothermal energy in providing sustainable, baseload power in regions with geothermal resources. The plant’s expansion over the years highlights the scalability of geothermal projects and the crucial role of steam turbines in this renewable energy sector.
- The Ivanpah Solar Electric Generating System, United States:
- Overview: Ivanpah is one of the largest concentrated solar power (CSP) plants in the world, located in California’s Mojave Desert. It has a capacity of 392 MW and uses mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto boilers, generating steam to drive turbines.
- Role of Steam Turbines: The steam turbines at Ivanpah are designed to operate with the variable steam input characteristic of CSP plants. They play a crucial role in converting solar energy into electricity, with the ability to start and stop quickly in response to solar conditions.
- Innovation: Ivanpah is an example of how steam turbines can be effectively integrated into renewable energy systems. The project demonstrates the potential for CSP technology to provide utility-scale renewable energy, supported by advanced steam turbine technology.
Industry Leaders
Several companies and institutions have made significant contributions to the development and deployment of steam turbines. These industry leaders have pioneered technological advancements and set benchmarks for efficiency and reliability.
- Siemens Energy:
- Overview: Siemens Energy is a global leader in the design and manufacture of steam turbines, with a portfolio that includes turbines for power generation, industrial applications, and marine propulsion. The company is known for its focus on innovation and efficiency.
- Key Contributions: Siemens has been at the forefront of developing high-efficiency steam turbines, including those for supercritical and ultra-supercritical applications. Their turbines are widely used in power plants around the world, contributing to both fossil fuel and renewable energy projects. Siemens is also a leader in digitalization, offering advanced monitoring and control systems that enhance turbine performance and reliability.
- General Electric (GE):
- Overview: General Electric is another major player in the steam turbine industry, with a long history of innovation and engineering excellence. GE’s steam turbines are used in a variety of applications, including power generation, industrial processes, and marine propulsion.
- Key Contributions: GE has been instrumental in advancing turbine efficiency through the development of high-performance blades, advanced materials, and integrated control systems. The company has also been a pioneer in the use of digital twins and predictive maintenance technologies, helping operators optimize turbine performance and reduce operational costs.
- Mitsubishi Power:
- Overview: Mitsubishi Power, a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, is a leading manufacturer of steam turbines, particularly in Asia. The company offers a wide range of turbines for power generation, including those for coal, nuclear, and gas-fired plants, as well as renewable energy projects.
- Key Contributions: Mitsubishi Power is known for its advanced steam turbine designs, which prioritize efficiency and reliability. The company has made significant strides in the development of ultra-supercritical turbines and has played a key role in the deployment of large-scale geothermal and biomass projects. Mitsubishi Power is also actively involved in R&D efforts focused on hydrogen-powered turbines and carbon capture integration.
Lessons Learned
The deployment of steam turbines across various industries provides valuable insights into the challenges and best practices associated with these technologies. Key lessons learned from these projects include:
- The Importance of Customization:
- Project-Specific Design: One of the most important lessons from successful steam turbine projects is the need for customization. Each project has unique requirements based on the type of fuel, operating conditions, and environmental regulations. Tailoring the design of the steam turbine to these specific conditions is crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability.
- Adaptation to Local Conditions: In projects like the Olkaria Geothermal Plant, adapting the turbine design to handle the specific characteristics of geothermal steam, such as high moisture content and corrosive gases, was essential for long-term success. This highlights the importance of understanding local conditions and incorporating them into the turbine design process.
- Efficiency as a Key Driver:
- Focus on Efficiency: Efficiency improvements have been a central focus in the development of steam turbines, driven by the need to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. Projects like the Taichung Power Plant demonstrate how supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam conditions can significantly enhance efficiency, leading to lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact.
- Innovation in Blade Design: Advances in blade design, such as 3D-aerodynamic blades and the use of advanced materials, have been critical in improving turbine efficiency. Lessons from industry leaders like Siemens and GE show that continuous innovation in turbine components is necessary to maintain competitiveness in the market.
- The Role of Digitalization:
- Embracing Digital Technologies: The integration of digital technologies, such as digital twins, AI, and real-time monitoring systems, has emerged as a best practice in the steam turbine industry. These technologies enable operators to optimize performance, predict maintenance needs, and reduce downtime, leading to improved overall efficiency and reliability.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The use of data analytics to monitor turbine performance and predict potential issues is becoming increasingly important. Industry leaders have demonstrated that data-driven decision-making can significantly enhance the operational efficiency and lifespan of steam turbines.
- Sustainability and Environmental Compliance:
- Sustainability Initiatives: The growing emphasis on sustainability has led to the adoption of cleaner energy sources, such as biomass, geothermal, and solar thermal, in steam turbine projects. Lessons from projects like Ivanpah show that steam turbines can play a key role in the transition to renewable energy, provided they are integrated with the appropriate technologies.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations is a critical aspect of steam turbine projects. The successful implementation of emission control technologies, as seen in the Taichung Power Plant, highlights the importance of adhering to regulatory standards to minimize environmental impact and ensure project viability.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Steam turbines have been a cornerstone of power generation and industrial applications for over a century, demonstrating remarkable adaptability and efficiency across various settings. This comprehensive exploration of steam turbines has covered their historical development, fundamental principles, design and manufacturing processes, and the wide range of applications in which they are employed.
- Fundamentals: At their core, steam turbines operate by converting thermal energy from steam into mechanical energy, which can then be used to generate electricity or drive machinery. The efficiency of this process depends on factors such as steam conditions, blade design, and the thermodynamic cycles employed, with the Rankine cycle being the most common.
- Design and Manufacturing: The design of steam turbines is a complex process that requires careful consideration of thermodynamics, materials science, and mechanical engineering. Advances in materials, such as superalloys and ceramic matrix composites, along with innovations in blade design and digitalization, are driving improvements in turbine efficiency and reliability. The manufacturing process, which includes casting, forging, machining, and heat treatment, ensures that turbines can withstand the extreme conditions under which they operate.
- Operation and Maintenance: Steam turbines require careful operation and regular maintenance to ensure their longevity and performance. Maintenance practices such as preventive and predictive maintenance, along with the use of advanced diagnostic tools, help prevent issues like blade erosion, rotor imbalance, and steam leakage. Proper operation, including control of steam quality and adherence to startup and shutdown procedures, is essential for maximizing efficiency and minimizing wear.
- Applications: Steam turbines are used in a wide variety of applications, from power generation in coal, nuclear, and geothermal plants to industrial processes in the petrochemical, pulp and paper, and steel industries. They also play a critical role in marine propulsion and are increasingly being integrated into renewable energy systems, such as concentrated solar power and biomass plants.
- Efficiency and Optimization: The efficiency of steam turbines is a key driver of their performance, with advancements in blade design, steam conditions, and energy recovery systems contributing to ongoing improvements. The use of digital twins, AI, and real-time monitoring systems is enhancing the ability to optimize turbine performance, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of turbine components.
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability: The environmental impact of steam turbines, particularly those powered by fossil fuels, is a significant concern. However, sustainability initiatives, such as the integration of renewable energy sources, the development of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam cycles, and the adoption of carbon capture technologies, are helping to mitigate these impacts and support the transition to a low-carbon future.
- Future Trends and Innovations: The steam turbine industry is poised for continued innovation, with advances in materials, digitalization, and integration with smart grids driving the future of the technology. Research into low-carbon and carbon-neutral technologies, such as hydrogen-fueled turbines and enhanced carbon capture systems, will play a critical role in the industry’s evolution. The challenges posed by environmental regulations, competition from alternative technologies, and aging infrastructure present both obstacles and opportunities for the industry.
The Future of Steam Turbines
As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, steam turbines will remain a vital component of power generation and industrial processes. Their ability to adapt to changing technologies, integrate with renewable energy systems, and improve efficiency will ensure their continued relevance in the coming decades.
The push for decarbonization and the need for more sustainable energy solutions will drive further innovation in steam turbine technology. The development of ultra-efficient steam cycles, the integration of digital technologies, and the exploration of new materials and designs will be essential for meeting the growing demand for clean, reliable, and efficient power.
Moreover, the role of steam turbines in emerging markets and in hybrid energy systems that combine traditional power generation with renewable sources presents significant growth opportunities. As these regions continue to industrialize and expand their energy infrastructure, the demand for steam turbines that can deliver high efficiency, reliability, and sustainability will increase.
In conclusion, steam turbines have a rich history of innovation and adaptation, and their future looks promising as they continue to evolve in response to the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century. The ongoing commitment to improving efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and integrating with advanced energy systems will ensure that steam turbines remain a cornerstone of global energy production for years to come.
Introduction to Power Generation with Steam Turbines

Steam turbines have been at the heart of power generation for over a century. Invented by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884, steam turbines quickly became the dominant technology for converting thermal energy into mechanical energy and, subsequently, into electrical energy. Their versatility and efficiency have made them the backbone of electricity generation worldwide.
In modern power generation, steam turbines are used in a variety of settings, from large-scale fossil fuel plants to renewable energy installations. They operate on the principle of converting the energy from high-pressure steam into mechanical energy by driving a rotor connected to a generator. The flexibility of steam turbines allows them to be integrated into diverse energy systems, including coal, nuclear, natural gas, geothermal, and solar thermal power plants.
The importance of steam turbines lies in their ability to efficiently produce large amounts of electricity. With advancements in technology, steam turbines have evolved to operate at higher temperatures and pressures, increasing their efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. These improvements have also led to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions per unit of electricity generated, making steam turbines a critical component in the transition to more sustainable energy systems.
Types of Power Plants Using Steam Turbines
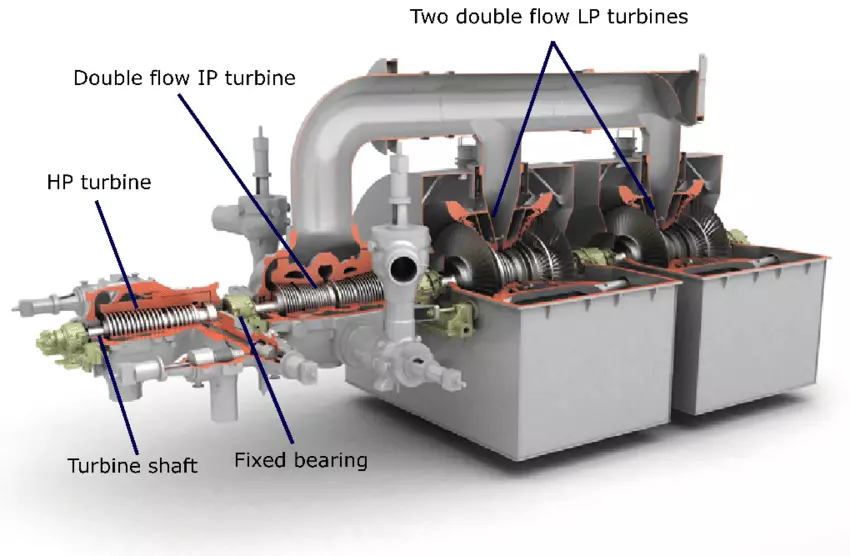
Coal-Fired Power Plants
Coal-fired power plants are among the most common applications of steam turbines. In these plants, coal is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam, which is then directed into a steam turbine to generate electricity. Despite the environmental challenges associated with coal, such as CO2 emissions and air pollution, it remains a significant energy source, particularly in developing countries.
The efficiency of coal-fired power plants has improved over the years, thanks to advancements in steam turbine technology. Supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam conditions, where steam is generated at temperatures and pressures above the critical point, allow for higher thermal efficiency. This means that more electricity can be generated from the same amount of coal, reducing the overall environmental impact.
Emission control technologies, such as flue gas desulfurization (FGD) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR), are employed to reduce the emission of pollutants like SO2 and NOx. Additionally, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies are being developed to capture CO2 emissions from coal plants, although these are still in the early stages of adoption.
Nuclear Power Plants

In nuclear power plants, steam turbines play a crucial role in converting the heat generated by nuclear fission into electricity. Nuclear reactors heat water to produce steam, which then drives a steam turbine connected to a generator. The steam turbines used in nuclear power plants are typically large and must be highly reliable, given the safety-critical nature of nuclear energy.
One of the key challenges in nuclear power generation is managing the steam conditions, which differ from those in fossil fuel plants. The steam produced in nuclear reactors is often at a lower temperature and pressure, which requires specific turbine designs to operate efficiently under these conditions. Additionally, the turbines must be capable of withstanding radiation and operating in a highly controlled environment.
The efficiency of nuclear power plants is influenced by the design of the steam cycle, with some plants employing reheat cycles to improve thermal efficiency. Advances in materials and turbine design continue to enhance the performance of steam turbines in nuclear applications, contributing to the overall reliability and safety of nuclear power generation.
Gas-Fired Power Plants (Combined Cycle)
Combined cycle power plants represent a significant advancement in the use of steam turbines. These plants combine a gas turbine with a steam turbine to maximize efficiency. In a combined cycle setup, a gas turbine generates electricity, and the waste heat from the gas turbine’s exhaust is used to produce steam, which then drives a steam turbine to generate additional electricity.
The efficiency of combined cycle power plants is among the highest of any power generation technology, often exceeding 60%. This is because the steam turbine effectively captures and utilizes energy that would otherwise be lost as waste heat. Combined cycle plants are also more flexible than traditional power plants, as they can be ramped up or down quickly in response to changes in electricity demand.
The integration of steam turbines in combined cycle plants has made natural gas a more attractive option for power generation, particularly in countries looking to reduce their reliance on coal and lower their carbon emissions. The ability to combine gas and steam turbines in a single plant allows for greater efficiency and lower environmental impact, making combined cycle plants a key component of the modern energy mix.
Geothermal Power Plants
Geothermal power plants harness the Earth’s natural heat to generate electricity, and steam turbines are central to this process. In these plants, steam is extracted from underground reservoirs and used to drive turbines. Geothermal steam often contains corrosive gases and minerals, which presents unique challenges for turbine design and operation.
The efficiency of geothermal power plants depends on the temperature and pressure of the geothermal steam. Higher temperature resources allow for the use of more efficient steam cycles, similar to those used in fossil fuel plants. However, geothermal plants typically operate at lower pressures, requiring turbines that can handle a wider range of steam qualities.
One of the key advantages of geothermal energy is its ability to provide baseload power, as geothermal resources are available 24/7. Steam turbines in geothermal plants must be robust and reliable, capable of operating continuously with minimal downtime. Innovations in turbine materials and designs are helping to improve the longevity and efficiency of geothermal turbines, making geothermal energy an increasingly important part of the renewable energy landscape.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Plants
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, where it heats a fluid to produce steam. This steam then drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP is unique among renewable energy technologies in that it can produce electricity even when the sun is not shining, thanks to thermal storage systems that store heat for later use.
Steam turbines used in CSP plants are designed to operate with variable steam inputs, as the intensity of sunlight can fluctuate throughout the day. The turbines must be capable of starting and stopping quickly and efficiently to match the availability of solar energy. CSP plants often use steam turbines with advanced blade designs and materials that can withstand the thermal cycling associated with intermittent solar input.
One of the key innovations in CSP is the integration of molten salt thermal storage, which allows the plant to store heat during the day and use it to generate steam at night or during cloudy periods. This ability to provide dispatchable power makes CSP with steam turbines a valuable addition to the renewable energy mix, particularly in regions with high solar irradiance.
Efficiency Considerations in Steam Turbine Power Generation
Efficiency is a critical factor in steam turbine power generation, as it determines how effectively fuel or energy resources are converted into electricity. Several factors influence the efficiency of steam turbines, including thermodynamic principles, technological advancements, and operational strategies.
Thermodynamic Efficiency
The efficiency of a steam turbine is largely governed by the principles of thermodynamics, particularly the Rankine cycle, which is the basic cycle used in steam power plants. The Rankine cycle involves four main processes: isentropic compression, isobaric heat addition, isentropic expansion, and isobaric heat rejection. The efficiency of this cycle can be improved through several methods:
- Superheating and Reheating: Increasing the temperature of steam (superheating) before it enters the turbine, or reheating the steam between turbine stages, can significantly improve efficiency by reducing the moisture content in the steam and allowing more energy to be extracted.
- Higher Pressure Ratios: Operating the turbine at higher pressures increases the amount of energy that can be extracted from the steam, improving overall cycle efficiency. Supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam conditions, where steam is generated at pressures above the critical point, represent the highest efficiency levels in modern power plants.
- Regenerative Feedwater Heating: Extracting steam from intermediate stages of the turbine to preheat the feedwater before it enters the boiler reduces the amount of fuel needed to produce steam, thereby improving the overall efficiency of the power plant.
Technological Advances
Advances in steam turbine technology have played a significant role in improving efficiency. Innovations in blade design, materials, and manufacturing techniques have allowed turbines to operate at higher temperatures and pressures, leading to greater energy conversion efficiency.
- Advanced Blade Designs: The design of turbine blades has a significant impact on efficiency. Modern blades are aerodynamically optimized to reduce losses due to turbulence and friction. The use of computational fluid dynamics (CFD) allows engineers to design blades that maximize the energy extracted from steam.
- High-Performance Materials: The development of advanced materials, such as nickel-based superalloys and ceramic matrix composites, has enabled steam turbines to operate at higher temperatures without compromising structural integrity. These materials resist creep, corrosion, and thermal fatigue, allowing for more efficient and durable turbine operation.
- 3D Printing and Precision Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing technologies, such as 3D printing, have enabled the production of turbine components with complex geometries that are optimized for efficiency. Precision manufacturing techniques also reduce material waste and improve the consistency and reliability of turbine components.
Operational Strategies
Operational strategies also play a crucial role in optimizing the efficiency of steam turbines. By carefully managing the operating conditions and load profiles, power plant operators can maximize the performance of steam turbines.
- Load Optimization: Steam turbines are most efficient when operating at or near their design capacity. However, power plants often experience varying demand throughout the day. By optimizing the load on the turbine, operators can maintain high efficiency even during periods of lower demand. Techniques such as load matching and peak shaving help ensure that turbines operate within their optimal range.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Control: Modern steam turbines are equipped with advanced monitoring and control systems that allow operators to adjust operating parameters in real-time. These systems use sensors and data analytics to monitor performance metrics such as steam temperature, pressure, and flow rate. By continuously optimizing these parameters, operators can improve efficiency and prevent issues before they lead to performance losses.
- Maintenance and Reliability: Regular maintenance is essential for maintaining the efficiency of steam turbines. Predictive maintenance, which uses data analytics to predict when components are likely to fail, helps minimize downtime and ensures that turbines continue to operate at peak efficiency. Proper lubrication, vibration analysis, and blade inspection are all critical components of an effective maintenance strategy.
Environmental Impact and Mitigation Strategies
Steam turbines play a central role in power generation, but they also contribute to environmental challenges, particularly when powered by fossil fuels. Understanding and mitigating these impacts is crucial for the sustainable operation of steam turbines.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The combustion of fossil fuels in steam turbines, particularly in coal and gas-fired power plants, is a significant source of CO2 emissions. These greenhouse gas emissions contribute to global warming and climate change, making it imperative to reduce the carbon footprint of steam turbine power generation.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS is a technology that captures CO2 emissions from power plants and stores them underground in geological formations. When integrated with steam turbines, CCS can significantly reduce the carbon emissions of fossil fuel-based power generation. While CCS is still in the early stages of adoption, ongoing research and development are focused on making it more cost-effective and scalable.
- Transition to Low-Carbon Fuels: Another strategy for reducing greenhouse gas emissions is transitioning from coal to lower-carbon fuels, such as natural gas, or even carbon-neutral fuels like biomass. Combined cycle power plants, which use both gas and steam turbines, offer higher efficiency and lower emissions compared to traditional coal-fired plants.
Air and Water Pollution
In addition to CO2, fossil fuel combustion in steam turbines also produces other air pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. These pollutants contribute to acid rain, smog, and respiratory problems in humans.
- Emission Control Technologies: Technologies such as flue gas desulfurization (FGD) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) are used to reduce SO2 and NOx emissions from power plants. Particulate matter can be controlled using electrostatic precipitators and baghouse filters. These technologies help mitigate the environmental impact of air pollution from steam turbines.
- Water Usage and Thermal Pollution: Steam turbines require significant amounts of water for cooling, which can impact local water resources. Additionally, the discharge of heated water back into the environment can cause thermal pollution, affecting aquatic ecosystems. To address these issues, power plants are increasingly adopting closed-loop cooling systems that minimize water withdrawal and reduce thermal discharge. Dry cooling systems, which use air instead of water, are also being implemented, particularly in water-scarce regions.
Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of steam turbines with renewable energy sources presents an opportunity to reduce the environmental impact of power generation. By leveraging steam turbines in conjunction with renewable energy technologies, such as biomass, geothermal, and concentrated solar power (CSP), it is possible to produce electricity with a lower carbon footprint.
- Biomass Power Generation: Biomass power plants use organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and waste, to produce steam that drives turbines. Biomass is considered carbon-neutral, as the CO2 released during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during the growth of the biomass. Steam turbines play a critical role in converting biomass energy into electricity, providing a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Geothermal and Solar Thermal: Geothermal power plants harness the Earth’s natural heat to produce steam, while CSP plants use concentrated sunlight to generate steam. Both technologies rely on steam turbines to convert thermal energy into electricity. These renewable energy sources produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making them attractive options for sustainable power generation.
Future Trends and Innovations in Steam Turbine Power Generation
The steam turbine industry is continuously evolving, with new technologies and trends shaping the future of power generation. These innovations are focused on improving efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing the flexibility of steam turbines in a changing energy landscape.
Decarbonization Initiatives
As the world moves toward decarbonization, steam turbines are being adapted to operate with low-carbon and carbon-neutral fuels. Hydrogen, in particular, is emerging as a promising fuel for steam turbines.
- Hydrogen-Fueled Steam Turbines: Hydrogen can be produced using renewable energy through electrolysis, resulting in a carbon-free fuel. Research is underway to develop steam turbines that can operate on hydrogen, either alone or in combination with other fuels. Hydrogen-fueled turbines have the potential to provide reliable, low-carbon power generation, especially in conjunction with renewable energy sources.
- Hybrid Energy Systems: Steam turbines are increasingly being integrated into hybrid energy systems that combine traditional power generation with renewable energy. These systems can provide continuous power while reducing carbon emissions. For example, a hybrid system might use a natural gas-fired steam turbine in combination with solar or wind power, with the turbine providing backup power when renewable sources are intermittent.
Digitalization and Smart Grids
Digital technologies are transforming the operation of steam turbines, making them more efficient, reliable, and responsive to grid demands.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being used to optimize turbine operations by analyzing data from sensors and control systems. These technologies can predict maintenance needs, optimize load distribution, and improve efficiency by adjusting operating parameters in real-time. AI-driven analytics are also helping to identify patterns and trends that can lead to better decision-making and improved turbine performance.
- Digital Twins: The concept of a digital twin, a virtual model of the steam turbine that runs in parallel with the physical machine, is becoming increasingly important in the industry. Digital twins allow operators to monitor turbine performance in real-time, simulate different scenarios, and optimize operations without risking the physical turbine. This technology is particularly valuable for predicting and preventing issues before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Smart Grid Integration: Steam turbines are being integrated into smart grid systems, which offer enhanced flexibility and efficiency in power generation and distribution. Advanced control systems and real-time monitoring enable steam turbines to respond quickly to changes in electricity demand, helping to balance the grid and prevent blackouts. The integration of steam turbines with energy storage systems, such as batteries, also enhances grid stability and allows for more efficient use of renewable energy.
Research and Development
Ongoing research and development (R&D) efforts are focused on advancing steam turbine technology to meet the evolving demands of the energy industry and address environmental challenges.
- High-Efficiency Steam Cycles: R&D is driving the development of supercritical and ultra-supercritical steam cycles, which operate at higher temperatures and pressures than conventional cycles. These advanced cycles offer higher thermal efficiencies, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that can withstand the extreme conditions of these cycles, making them more viable for widespread adoption.
- Carbon Capture Integration: Integrating carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies with steam turbines is a key area of research aimed at reducing CO2 emissions from fossil fuel-based power generation. Ongoing R&D efforts are focused on improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of CCS, making it a viable option for large-scale deployment.
- Advanced Materials and Coatings: The development of new materials and coatings that can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments is essential for improving the durability and efficiency of steam turbines. Research into advanced coatings, such as thermal barrier coatings and anti-corrosion treatments, is helping to extend the life of turbine components and reduce maintenance costs.
Conclusion
Steam turbines have been a cornerstone of power generation for over a century, and their role continues to evolve in response to changing energy needs and environmental challenges. This comprehensive overview of steam turbine power generation has highlighted the versatility, efficiency, and sustainability of steam turbines across a range of applications.
From coal-fired and nuclear power plants to renewable energy systems like geothermal and concentrated solar power, steam turbines are critical to producing reliable and efficient electricity. Technological advancements, including supercritical steam cycles, advanced blade designs, and digitalization, have significantly improved the performance of steam turbines, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly.
As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, steam turbines will play an essential role in decarbonization efforts. The integration of hydrogen as a fuel, the adoption of carbon capture technologies, and the development of hybrid energy systems are just a few of the ways steam turbines are being adapted to meet the demands of a more sustainable energy future.
The future of steam turbines is bright, with ongoing research and innovation driving continued improvements in efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance. As digital technologies like AI and digital twins become more prevalent, steam turbines will become even more integrated with smart grid systems, enhancing their flexibility and responsiveness to changing energy demands.
In conclusion, steam turbines will remain a vital component of global power generation for years to come. Their ability to adapt to new technologies and integrate with renewable energy sources ensures that they will continue to play a key role in the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
EMS Power Machines
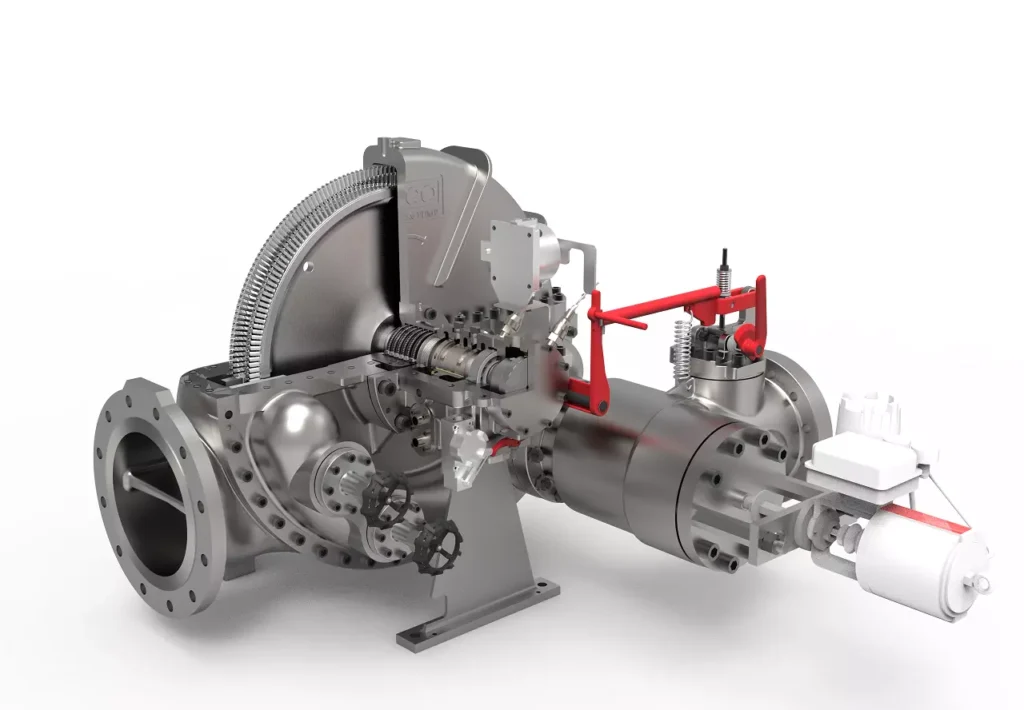
We design, manufacture and assembly Power Machines such as – diesel generators, electric motors, vibration motors, pumps, steam engines and steam turbines
EMS Power Machines is a global power engineering company, one of the five world leaders in the industry in terms of installed equipment. The companies included in the company have been operating in the energy market for more than 60 years.
EMS Power Machines manufactures steam turbines, gas turbines, hydroelectric turbines, generators, and other power equipment for thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric power plants, as well as for various industries, transport, and marine energy.
EMS Power Machines is a major player in the global power industry, and its equipment is used in power plants all over the world. The company has a strong track record of innovation, and it is constantly developing new and improved technologies.
Here are some examples of Power Machines’ products and services:
- Steam turbines for thermal and nuclear power plants
- Gas turbines for combined cycle power plants and industrial applications
- Hydroelectric turbines for hydroelectric power plants
- Generators for all types of power plants
- Boilers for thermal power plants
- Condensers for thermal power plants
- Reheaters for thermal power plants
- Air preheaters for thermal power plants
- Feedwater pumps for thermal power plants
- Control systems for power plants
- Maintenance and repair services for power plants
EMS Power Machines is committed to providing its customers with high-quality products and services. The company has a strong reputation for reliability and innovation. Power Machines is a leading provider of power equipment and services, and it plays a vital role in the global power industry.
EMS Power Machines, which began in 1961 as a small factory of electric motors, has become a leading global supplier of electronic products for different segments. The search for excellence has resulted in the diversification of the business, adding to the electric motors products which provide from power generation to more efficient means of use.
